Class 7 - How to get Bitcoin?
🎥 Class Video
👉 Click here to watch on YouTube
Full Script
Class 7 - How to get bitcoin?
The race to own bitcoin has already begun and if you're thinking of owning a whole bitcoin, you'd better hurry up, because time is running out and it's going to get harder and harder. But the good news is that there are 2.1 quadrillion satoshis and you can gradually accumulate fractions of bitcoin until you reach your entire bitcoin.

Today, the world has around 8 billion people. As Bitcoin has a maximum issuance limit of 21 million units, which will be issued until the year 2140, and most of these have already been mined, this means that if everyone in the world wanted to own Bitcoin, they could each have a maximum of 0.002625 BTC. This is equivalent to approximately 260,000 satoshis, or about 245 dollars, considering the current price of 94,000 dollars per bitcoin.
There isn't enough bitcoin for everyone in the world, not even for all the millionaires. But there are plenty of satoshis to be distributed among all the inhabitants of the Earth. That's because 1 bitcoin is made up of 100 million satoshis, which makes a whole bitcoin just a form of rounding.
Remember that this estimate is based on a limit of 21 million bitcoin. However, it's unlikely that all these bitcoin are actually available, since around 20% of them have been lost and are in inaccessible wallets. This makes bitcoin even more scarce than you might think.

There are three ways to own bitcoin. The first and most classic form is mining. It is through mining that new bitcoin enter the market and it is a way for you to receive bitcoin directly from the network by doing work for it. You employ computing power, help mine a block and receive bitcoin as a reward. Of course, nowadays you need powerful equipment to mine a large amount of bitcoin, but it's something you can study, specialize in and start competing in mining.
The second way to own bitcoin is to buy it from someone who owns it. Today there are also platforms that facilitate this purchase, such as exchanges, platforms, vouchers and even banks that sell bitcoin. Today it's much easier to buy bitcoin than it was 10 years ago.
And the most independent and cypherpunk way to get any bitcoin without mining it is to accept it as payment in exchange for products or services you offer. Let's understand how each of these works.

Mining is a way of receiving bitcoin directly from the network, without having to buy from another person or platform. Mining has become a highly specialized industry, with operations ranging from small individual miners to large mining farms. These sites use advanced technologies and, in many cases, harness the energy that would be wasted by less efficient industries.

You don't need a large mining facility to get started. It is possible to mine Bitcoin at home, as long as you are willing to learn how the machines work, carry out maintenance, optimize energy efficiency and have a good understanding of electrical wiring. After all, it was home mining that started it all and it is through home mining that this practice could become increasingly accessible and common in the future.

Nowadays, there are machines like the Bitaxe and the Nerdminer, which have reduced computing power compared to the powerful ASICs. Nevertheless, they can be connected to a mining pool to receive small rewards in satoshis or even used to try their luck at solo mining. Mining solo and finding a block is like hitting the lottery -- the odds are slim, but the prize is worth it.
Bitcoin mining is constantly evolving, and who knows, maybe in the future even kitchen appliances will be helping to mine Bitcoin! In addition to mining, you can also buy bitcoin from another person or company that has it.

And when it comes to buying bitcoin, there are several ways to do it. You can buy through platforms that work like digital currency exchanges. You can buy from someone else who has bitcoin, the famous P2P (peer-to-peer). You can buy vouchers or giftcards that can be redeemed in Bitcoin. You can buy through social networks that have channels for buying and selling bitcoin, such as Telegram or Nostr. And finally, even banks now sell Bitcoin and you can buy through them.
But what are the advantages and disadvantages of each?

Exchanges are companies that connect buyers and sellers, ensuring that both sides receive what is being traded in a practical way. The exchange is an intermediary between two people who don't know each other and who want to trade bitcoin.
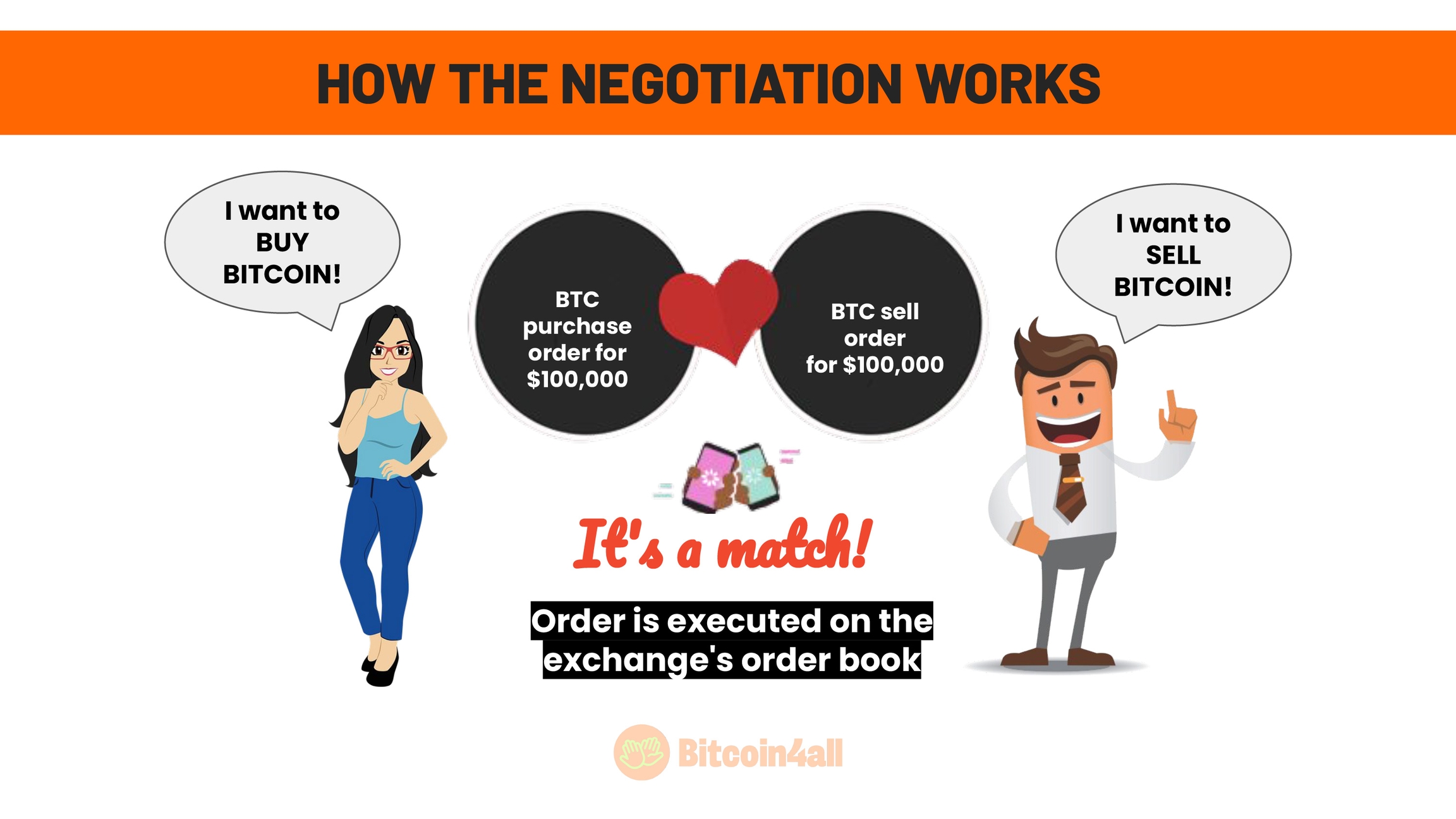
So, for example, here we have Ana and John. They both have accounts at the same exchange and they don't know each other and won't meet. Ana wants to buy bitcoin and John wants to sell bitcoin. The two put the exchange in order.
Ana placed an order to buy bitcoin at 100 thousand dollars and John placed an order to sell bitcoin at 100 thousand dollars. So, here in this example, one wants to buy and the other wants to sell at the same value as the price per bitcoin at that moment. And so this negotiation was a match. Both parties' orders are executed at hte order book, John's bitcoin balance is settled in fiat and Ana receives the bitcoin balance that was previously John's in her account at the exchange.
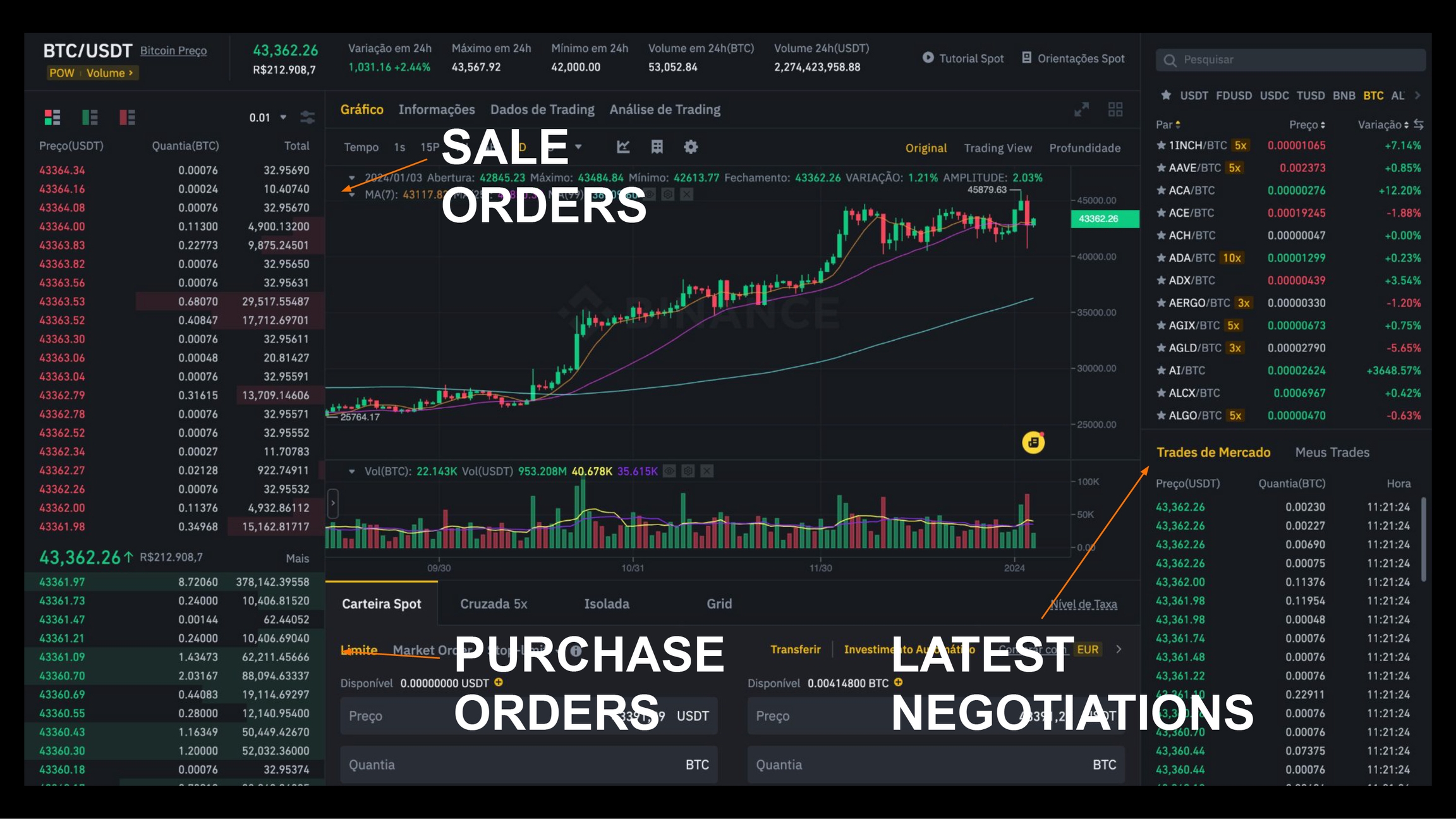
Those buy and sell orders I mentioned are placed through a mechanism called an order book. This is the classic way of trading on an exchange, but today there are other possibilities besides this. There are simplified ways where you don't see these orders.
In this image we can see the list of sell orders in red and the list of buy orders in green below. Each order in the book includes the price at which someone is willing to buy or sell bitcoin, as well as the amount of bitcoin they want to buy or sell at that price. Orders are generally organized in price order. There you can see that the buy orders are organized from the highest to the lowest price that buyers are willing to pay. Sell orders are organized from the lowest to the highest price that sellers are willing to accept.

The great advantage of buying in exchanges is practicality. In just a few minutes, you can easily open an account, transfer fiat currency and start buying bitcoin. However, if you're looking for privacy, this isn't the best way to buy, because these are companies. As such, they follow the regulations of their countries. Most ask for KYC, which stands for know your customer -- that is, customer data --, at the time of registration. They usually have a lower limit for negotiating with basic data and if you want to negotiate higher amounts, they ask for more documents.

And although today the market is more mature and it is relatively safe to buy from these companies, there are still risks. Today, if you want to become an entrepreneur and open an exchange, you'll have to go through a lot of, as well as ask the government for permission to operate in this market. You'll also have to follow the rules of the country where you're opening the company. Although they are not banks, exchanges function like banks and are under the scrutiny of regulators.
The idea of regulation is to eliminate bad actors from the market, but it still doesn't prevent these companies from failing due to mismanagement or hacks. On exchanges, the biggest risks are hacker intrusions and leaks of confidential data. In the past, hackers have broken into exchanges and stolen bitcoin balances, leading several exchanges to close their doors.

Another risk is bankruptcy. In the event that the partners and managers don't know how to manage the business, or carry out illegal operations, as happened with FTX, and the exchange goes bankrupt. If a hacker attack takes place or the exchange goes bankrupt, it could take years of legal proceedings to get your money back. You might as well never get your bitcoin back. Many people have lost their bitcoin this way.
(slide 179)[https://github.com/areabitcoin/Bitcoin-4-All/blob/581180cca19224baeee0f17e57e852216db40982/Bitcoin%204%20All%20-%20English/Slides/Class%207/slide-13.jpg] That's why exchanges are not wallets and you shouldn't leave your bitcoin in them for prolonged periods of time. An exchange is an access platform just for you to buy and withdraw Bitcoin for your own custody. Leaving your bitcoin on an exchange means exposing yourself to the risk of the platform going bankrupt or being hacked and taking your coins with it.
These are platforms that facilitate exchanges between people, but they don't provide the private keys of their clients' wallets, only the address. That is why bitcoin isn't yours on the exchange, since you don't have the private keys that allow you to move your coins independently. We'll talk more about this in the following lessons on desks and sovereignty.
Now let's move on to the P2P forms of purchase.

Do you remember the Bitcoin whitepaper? What was written on it? Satoshi wrote in the title of the white paper "Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system". At the beginning of the Bitcoin network, negotiations were basically done like this, directly between people. Nowadays, even with so many exchanges and digital accounts to choose from, the P2P way of trading remains firm and strong and will probably never cease to exist. After all, no matter how many countries ban the use of Bitcoin, it is decentralized and open source, so there's no stopping people from trading with each other in a P2P way.

The biggest advantage of buying P2P is that there is less bureaucracy and a little more privacy. So, for example, when buying via P2P you don't need to send all the documents that an exchange often asks for, do facial recognition or send proof of income and address. Some exchanges are as bureaucratic as banks.
Another advantage is that P2P sends the bitcoin balance directly to the address, which could be your cold wallet, for example. It's very practical and one less step for you to take. On the other hand, it has also some disadvantages and risks. As everything is usually done directly online, there is no intermediary company, so you have to make sure that the P2P you choose is trustworthy. You need to trust that the person won't disappear with your money and that you'll get the bitcoin equivalent back in your wallet. There are P2Ps who have been working in the market for a long time and who are honest people, but there are also scammers, as is the case with every market.
So how do you detect that a P2P is a scammer? Firstly, a P2P will never contact you via Facebook Messenger, Instagram, Telegram or even WhatsApp offering bitcoin. No serious P2P does that. If they contact you in this way, there's a good chance it's a scam.
But where can you find reliable P2P sellers and buyers? Anyone can sell you bitcoin, whether it's a friend who has bitcoin and needs fiat or someone who does it for a living. Many P2Ps work on their own, with their own website or connected to an exchange, but it's best to find a referral from someone you trust. Another way is to buy on platforms such as Bisq and Hodl Hodl, which connect people to each other.

There are a total of 4 steps to buying via P2P.
The first is to already have an address in a Bitcoin wallet. You'll learn how to do this in the next Bitcoin 4 All lessons.
Secondly, you'll contact a trusted P2P and ask for a quote for the amount you want to buy. Once the quote has been approved, you send the amount in fiat and your bitcoin address so that the P2P can send you the balance. Finally, you wait for the receipt and monitor via a tracking code on the Bitcoin network that the P2P will provide you with, a transaction ID. That's it!
Another way to buy Bitcoin is by using vouchers.

Vouchers are giftcards. With them, you can buy an amount and redeem it in your digital wallet, as is the case with AZTECO and Bitrefill. Buying Bitcoin through vouchers is more private than through exchanges and you receive the redeemed balance directly in your wallet.

There are also online platforms such as Robosats and Mostro on the NOSTR protocol that allow the buying and selling of bitcoin in a P2P manner in discussion groups without necessarily having a centralized company intermediating the operations. This type of purchase generally offers more privacy and less data linkage to your Bitcoin purchases.
The important thing with this type of purchase is to make sure you're using the right platform and not a fake version of them.

Nowadays, banks and digital accounts also allow you to buy Bitcoin. The main difference between these digital accounts and exchanges is that, in digital accounts, you buy Bitcoin directly from the institution, while in exchanges, the purchase is made by other people who have entered sell orders on the platform.
Regardless of where you acquire your bitcoin, it is essential to transfer them from these platforms to your own wallet and avoid leaving them in the custody of third parties. Both banks and exchanges are subject to the same risks, such as bankruptcy, hacker attacks or even government seizures.

It's 2025 and traditional financial institutions are vying to offer Bitcoin ETFs. ETF stands for Exchange Traded Fund. These funds allow investors to buy and sell shares directly on the stock exchange, in a comparable way to shares, and can be used to trade several types of assets, such as commodities and, now, Bitcoin.
Bitcoin spot ETFs aim to replicate the price of Bitcoin on the spot market by tracking its price. The main advantage of Bitcoin ETFs is that they offer a regulated way for companies and investors, who normally wouldn't or couldn't hold Bitcoin in their own custody, to gain indirect exposure to Bitcoin.
These ETFs have created a bridge between Bitcoin and the traditional financial market, establishing Bitcoin as a new recognized asset class in this environment. In addition, ETFs increase the demand for Bitcoin, since, theoretically, funds need to buy and sell Bitcoin as investors acquire or dispose of ETF shares. In other words, they could not operate with Bitcoin without these transactions being backed up by purchases or sales of real Bitcoin on the spot market.
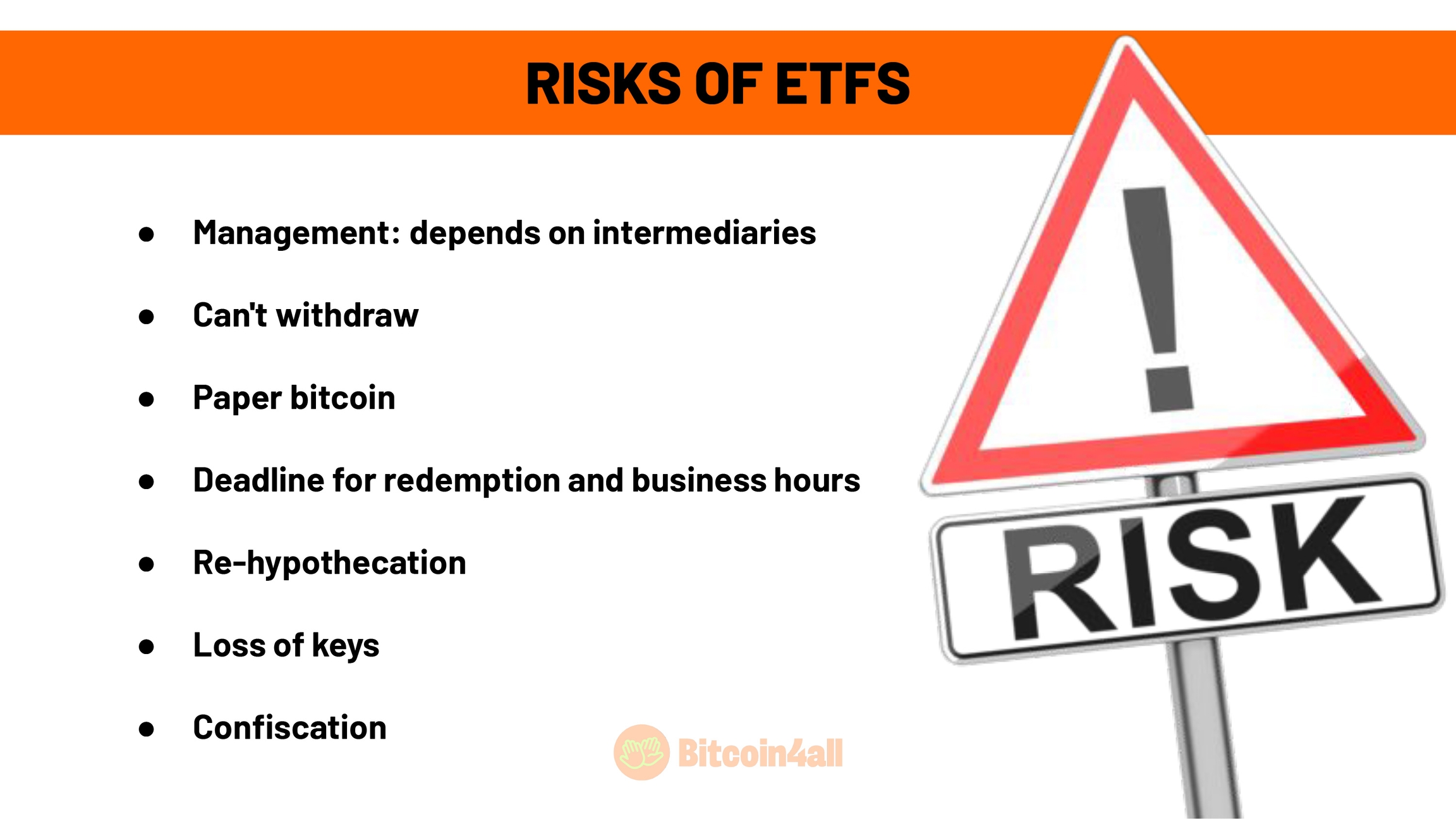
Just be careful! ETFs are not real Bitcoin. They are paper Bitcoin that only represent the price of Bitcoin. It has neither the monetary properties nor the network effect of Bitcoin. They need a manager to issue these papers and they need to trust these institutions.
You can't withdraw your bitcoin to your wallet, you have to sell it and convert it to fiat. At least so far, there's no way to buy an ETF and withdraw bitcoin to your own wallet. This means that when you buy an ETF you don't actually own bitcoin, you're depending on intermediaries to do the custody for you. This defeats the whole purpose of Bitcoin. You end up being exposed only to the price, but you don't have the freedom to use your money as you wish.
In addition, there are cash redemption and trading deadlines within the opening hours of the exchanges, during business hours. Bitcoin, on the other hand, works 24 hours a day, every day of the week. If the price falls or rises over the weekend, the ETF will only reflect this on Monday. You spend the weekend and holidays unable to buy or sell.
This time gap is an eternity if tense news breaks about the possibility of bankruptcy or something similar.
Another risk is rehypothecation, whereby issuers carry out risky transactions with their clients' bitcoin, which may only turn up years later and be a headache. It would be something like using their clients' BTC as collateral for loans to buy other assets. That's not such an unrealistic thing to happen: in fact, that's basically how FTX went bankrupt in 2022. This type of operation, using clients' money, is obviously illegal, but the market does things backstage that we can't even imagine. In this rehypothecation situation, if the price of Bitcoin plummets, they could be liquidated and lose their customers' BTC.
Another risk is the mismanagement of the bitcoin private keys they have under management. Some managers custody their clients' bitcoin, but most ETFs use exchanges to custody the bitcoin they sell. Coinbase, for example, holds the bitcoin of most American ETFs. In these cases, the risk is that these third-party custodians, these exchanges, go bankrupt or mismanage the keys.
Another risk is the government's apprehension. If Bitcoin becomes a global reserve asset and this threatens global hegemonies, a government could easily confiscate the BTC of these regulated players. It's easier to confiscate money from these intermediaries than from people who keep their own keys. From one day to the next they can make up a national holiday and people might lose access to their own assets. When it comes to bitcoin in regulated banks and management companies, it's quite easy for governments to confiscate it.

And finally, the most sovereign way to get bitcoin is to offer your work, products and services, your time, in exchange for bitcoin. You turn your work and profit margin into an accumulation strategy, getting paid directly without having to convert anything. It all goes straight into your wallet. You can even save on fees by doing this.
There are websites and platforms such as Bitcoiner Jobs where you can search for jobs with companies that pay in bitcoin. Whether it's temporary or a full-time job. Behance also has a tab where you can choose to pay for design work in Bitcoin.
You can offer your services to other bitcoiners you know and start your own local circular economy with your friends. After all, for you to be paid in bitcoin, someone has to pay you in bitcoin. If a group uses bitcoin as its currency, it's much easier to get started with them. Besides, if you generate incentives, such as discounts, people will be willing to spend a few sats to get that discount if your product is good. After all, nobody exchanges bitcoin for a poor-quality product.
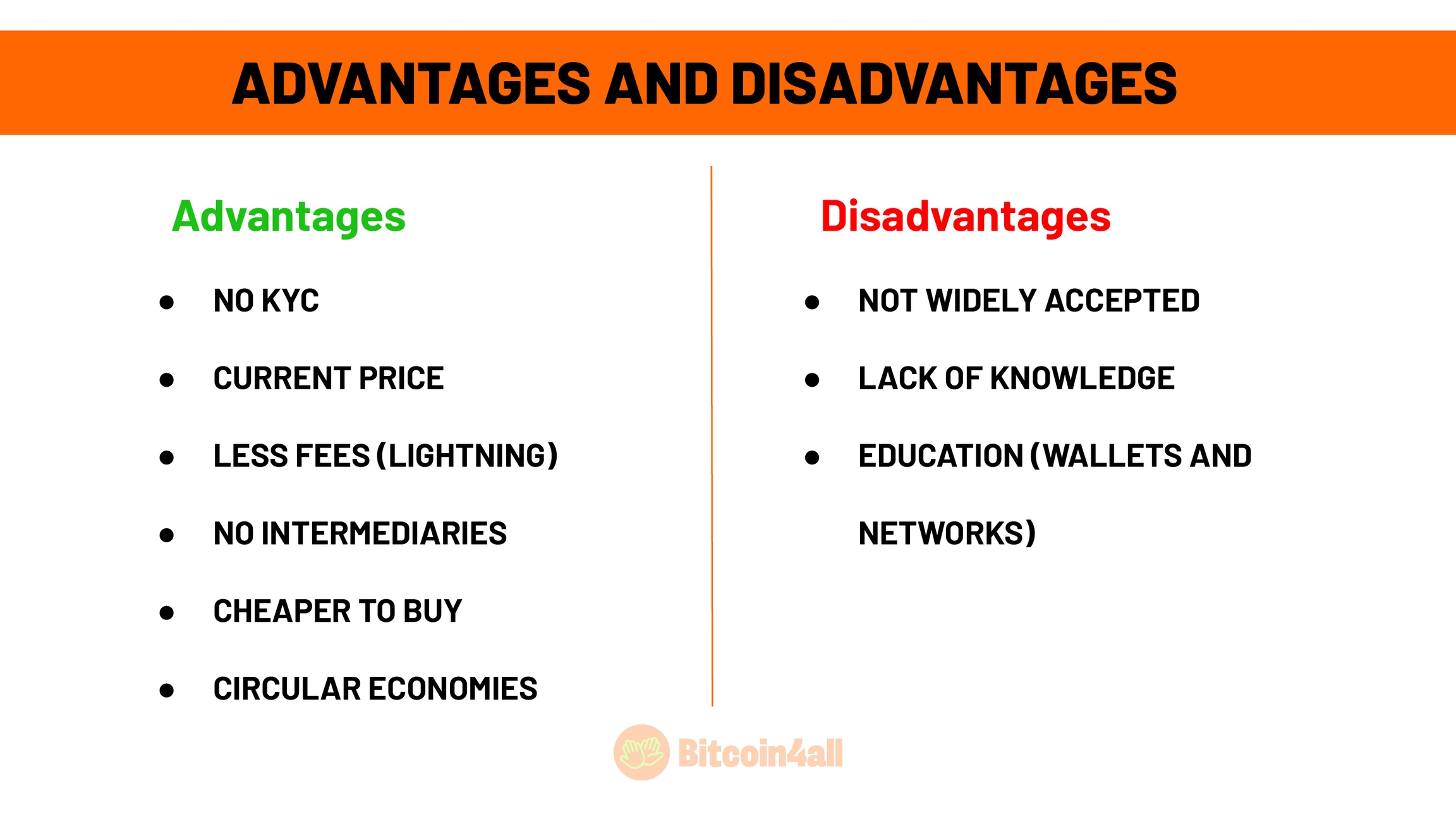
Accepting bitcoin as payment offers several advantages that can modernize and simplify financial operations. One of the main ones is the lack of KYC (Know Your Customer). The Bitcoin network doesn't force anyone to identify themselves. You can just download a wallet and start receiving bitcoin. It also has the advantage of using the current exchange rate. When you receive payments in bitcoin, the amount is transferred immediately, at the current rate, avoiding the huge spreads and delays common in transactions that depend on financial intermediaries.
The Lightning Network also makes life much easier, as it enables fast transactions with extremely low fees, making it especially advantageous for small payments. Compared to the fees charged by credit cards or other payment gateways, this represents huge savings in fees for merchants who can pass them on as a discount to customers.
When you receive Bitcoin directly, there is no need for banks or payment companies, which reduces costs, speeds up receipt and avoids problems with fraudulent chargebacks or unjustified cancellations.
For those who already accept Bitcoin, receiving directly from customers is cheaper than buying from exchanges or platforms that charge additional fees. This practice also stimulates circular economies, where payments and receipts in Bitcoin strengthen adoption and local use, as well as reduce the need to convert to fiat currencies, saving time and money.
But it also has some disadvantages that need to be considered. One of them is that few people use Bitcoin for payments. Although adoption is growing, the number of people paying in Bitcoin is still not large. Besides, there are a lot of people who don't want to spend at all: they just want to receive.
Lack of knowledge is also a challenge. Many people even want to receive but don't understand how it works, find it difficult and get discouraged. Accepting Bitcoin requires knowledge of how to set up a secure digital wallet and, in many cases, the use of the Lightning Network for fast and cheap transactions. For those just starting out, this learning curve can be an obstacle.
But little by little, circular economies are becoming better known, and those who want to receive and pay in Bitcoin are starting to create a local microcosm of P2P exchanges.
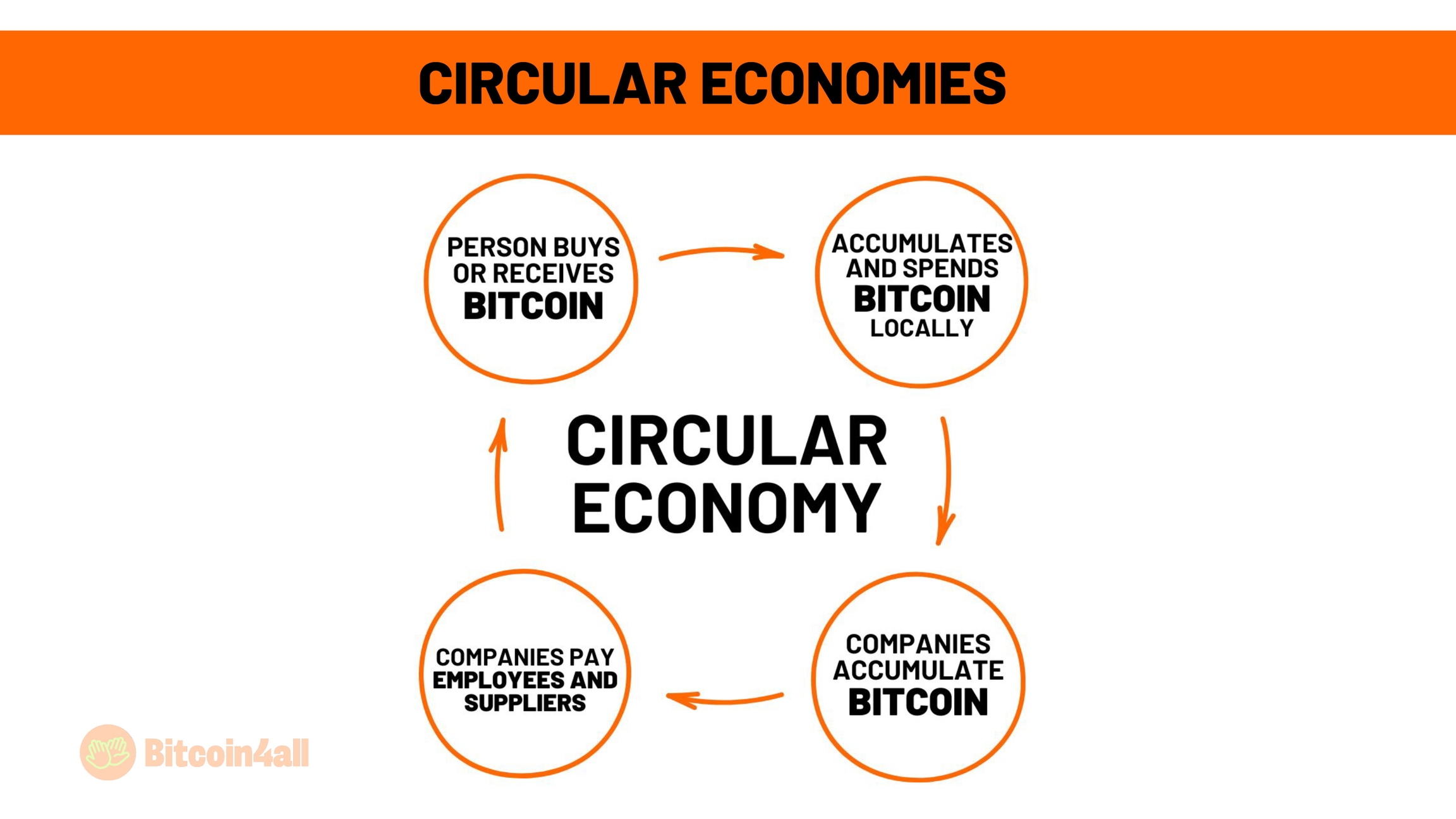
A circular Bitcoin economy is when Bitcoin is used continuously within a sustainable cycle, without the frequent need to convert to fiat currencies. This model increases adoption, strengthens local communities and reduces dependence on financial intermediaries, creating a more autonomous and efficient system.
A circular economy begins with the acquisition or receipt of Bitcoin. You can acquire Bitcoin by mining it, buying it on exchanges, accepting it as payment for products or services or even receiving it as a salary. By doing so, it becomes a decentralized and global asset that can be used without the need for banks or intermediaries.
Instead of converting your Bitcoin into fiat currency, you can use Bitcoin directly to pay for products and services at local businesses that accept it. Merchants who receive Bitcoin can choose to keep part of their Bitcoin revenue as a form of savings with the potential to appreciate over time, or they can choose to pay employees and suppliers who also accept Bitcoin.
This continuous cycle of payments and receipts reduces the need for conversions to fiat and increases the use of Bitcoin as money.
Bitcoin's circular economy concept is a natural evolution of adoption, increasing financial independence, strengthening local economies and economic sustainability. For communities that embrace this model, Bitcoin becomes not only a medium of exchange, but also a catalyst for innovation and economic resilience.
Well, I hope this lesson has helped you understand that there are multiple ways to own Bitcoin. Now it's up to you to experiment and see which of these ways suits you best. The best thing about it is that you can use all these mechanisms to keep accumulating. I'll see you in the next class.
Additional Resources
📢 Share this lesson!
Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Telegram
📈 Your Course Progress
Class 7 de 10 (70% completo)
Last updated
