Class 3 - Why Bitcoin is better money
🎥 Class Video
👉 Click here to watch on YouTube
Full Script
Class 3 - Why Bitcoin is better money
In the previous lesson, you learned about the history of money and why fiat money is an ice cube. Now, in this lesson, you will understand how Bitcoin solves many of the age-old problems that both fiat money and gold failed to solve.
The first step to understanding why Bitcoin is better money is to understand that it has better monetary properties. The main one is to preserve value. If fiat money melts in value, Bitcoin is the opposite, it gains value.
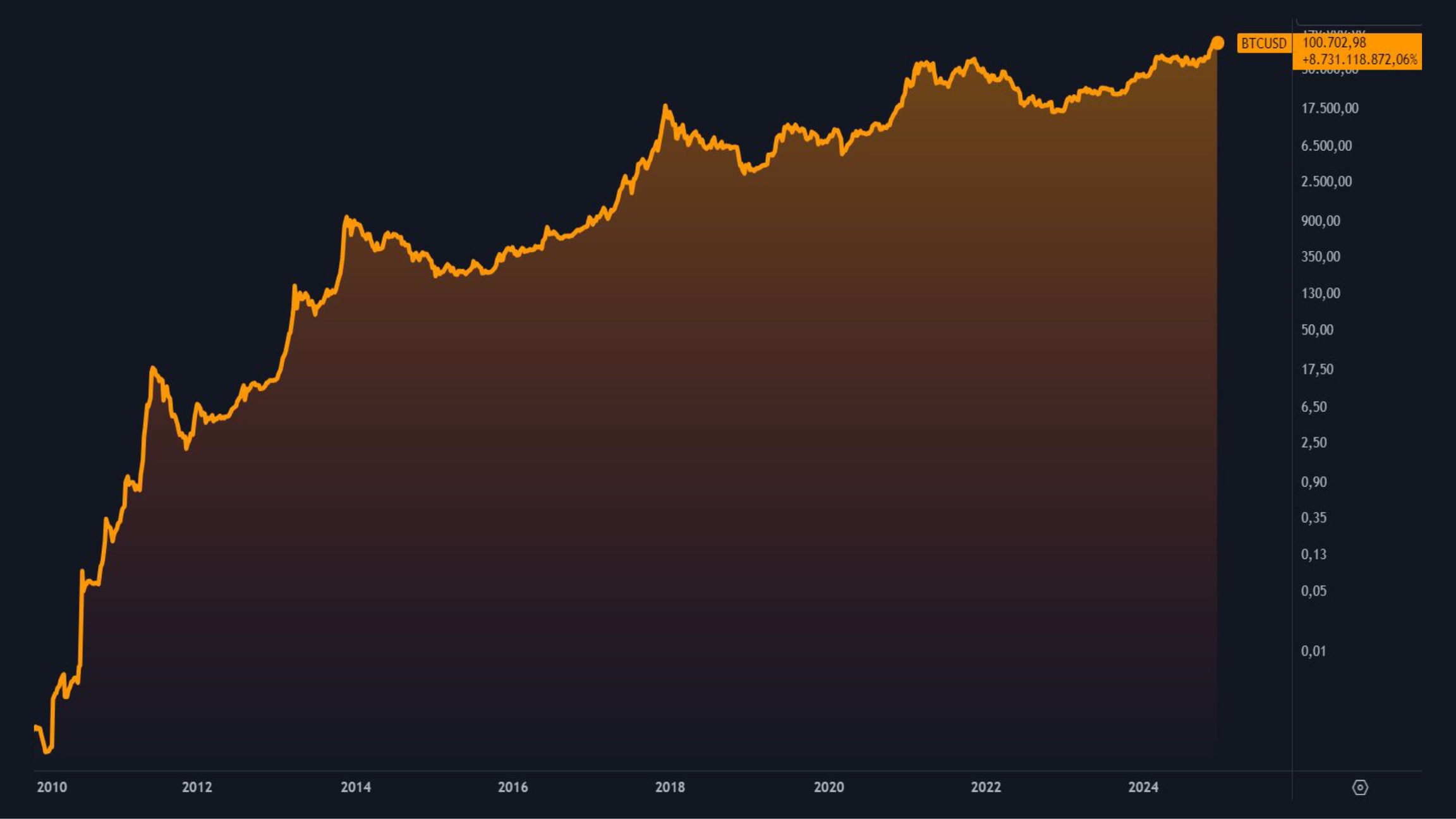
Since its launch in 2009, Bitcoin has appreciated impressively. Initially, it had no price: its value was literally zero. However, over the years, Bitcoin has accumulated a growth of over 8 billion percent in dollars between 2010 and 2024. In 2024, it reached the 100,000 dollars per unit, consolidating its trajectory -- volatile in the short term, but one of continuous growth over 15 years.
Bitcoin is fundamentally different from fiat currencies. The term "fiat" derives from Latin and means "let it be done". It refers to money made by decree, imposed by governments through laws of forced circulation: money adopted artificially instead of an adoption due to its natural monetary properties. People use fiat currencies because they are forced to, while Bitcoin and gold are freely adopted because of their natural properties.
As I mentioned in the previous lesson, gold has unique atomic properties, formed by cosmic processes such as nuclear shocks during the formation of the Earth. Bitcoin, on the other hand, is based on mathematical properties that are protected by its decentralized structure. This decentralization, both in its code and in its records, ensures that no one, no matter how powerful, can change the fundamental properties of Bitcoin -- just as no one can change the natural atomic properties of gold. To change gold would be to recreate any other metal but real gold. The same thing happens with Bitcoin. That's why, although there are millions of cryptocurrencies, none of them can do what Bitcoin does and none of them even comes close to the relevance that Bitcoin has.
For these reasons, both gold and Bitcoin have valued over time, while fiat currencies, which depend on arbitrary political and economic decisions, constantly lose value.
Central banks justify the existence of fiat currencies and their monetary policies by claiming that they serve to "control the economy and ensure financial stability". But reality shows a different story. Since 1971, when the gold standard was abandoned, we have faced recurrent global and local economic crises. In practice, the Central Bank can't even protect the value of its own currency, which should be its main responsibility.
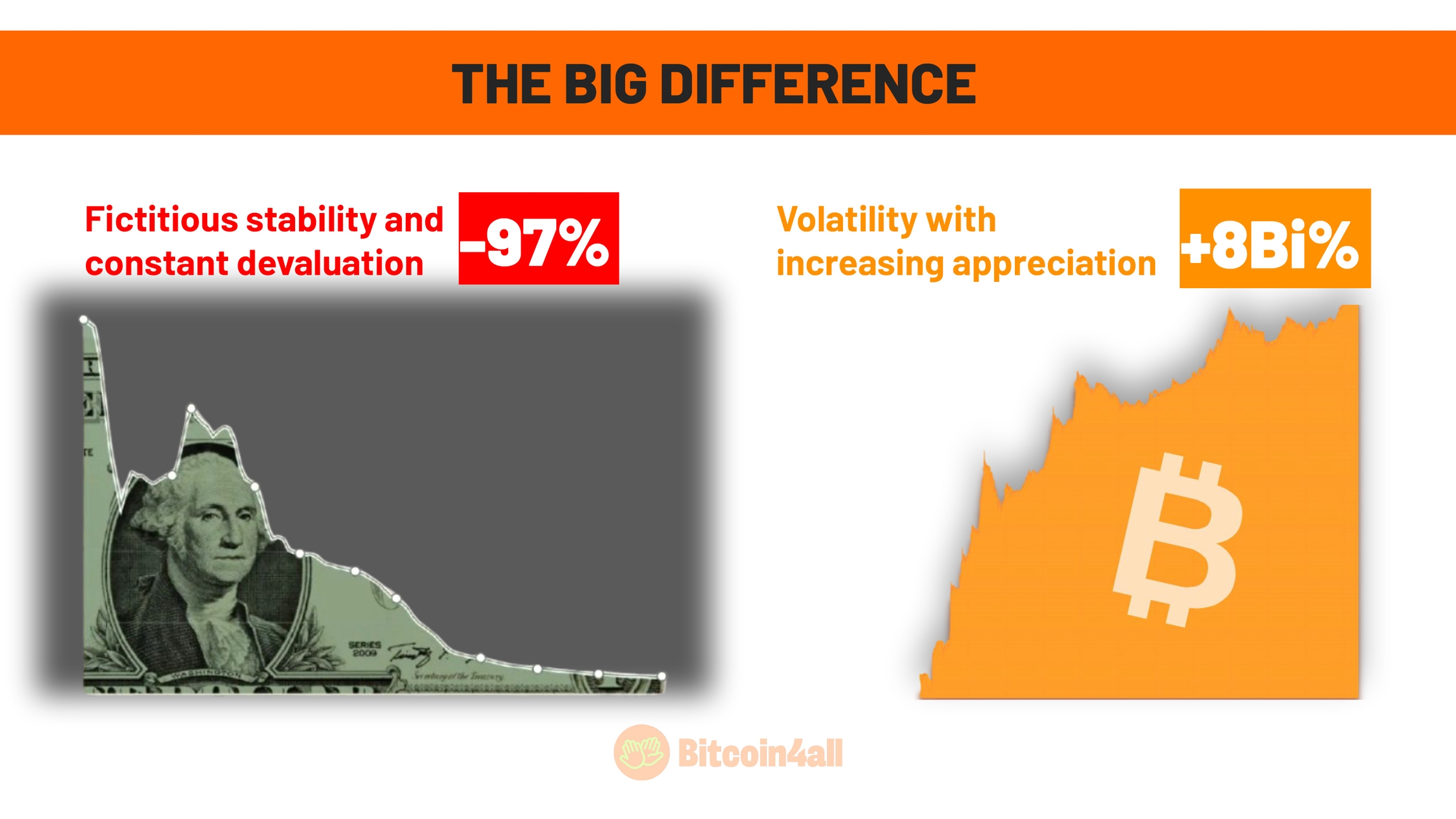
Many economists and investors critical of Bitcoin argue that it is too volatile to be considered money. However, they forget that fiat currencies are also extremely volatile, just in a different way. The so-called "stability" of fiat money is an illusion, as it constantly loses value over time. Bitcoin, on the other hand, despite its volatility, has shown a significant increase in value and purchasing power over the years.
For example, the real, the Brazilian currency, has lost 87% of its value since it was implemented, and the dollar, the US currency, has lost 97% of its value since FED's creation in 1913. In contrast, Bitcoin has increased in value by around 8 billion percent since it was created in 2009. In just 16 years, Bitcoin has protected and expanded purchasing power more effectively than any national currency.
This is because Bitcoin has superior monetary properties. Just as gold was historically adopted as money by various civilizations because of its monetary properties, Bitcoin has even more robust characteristics as money.
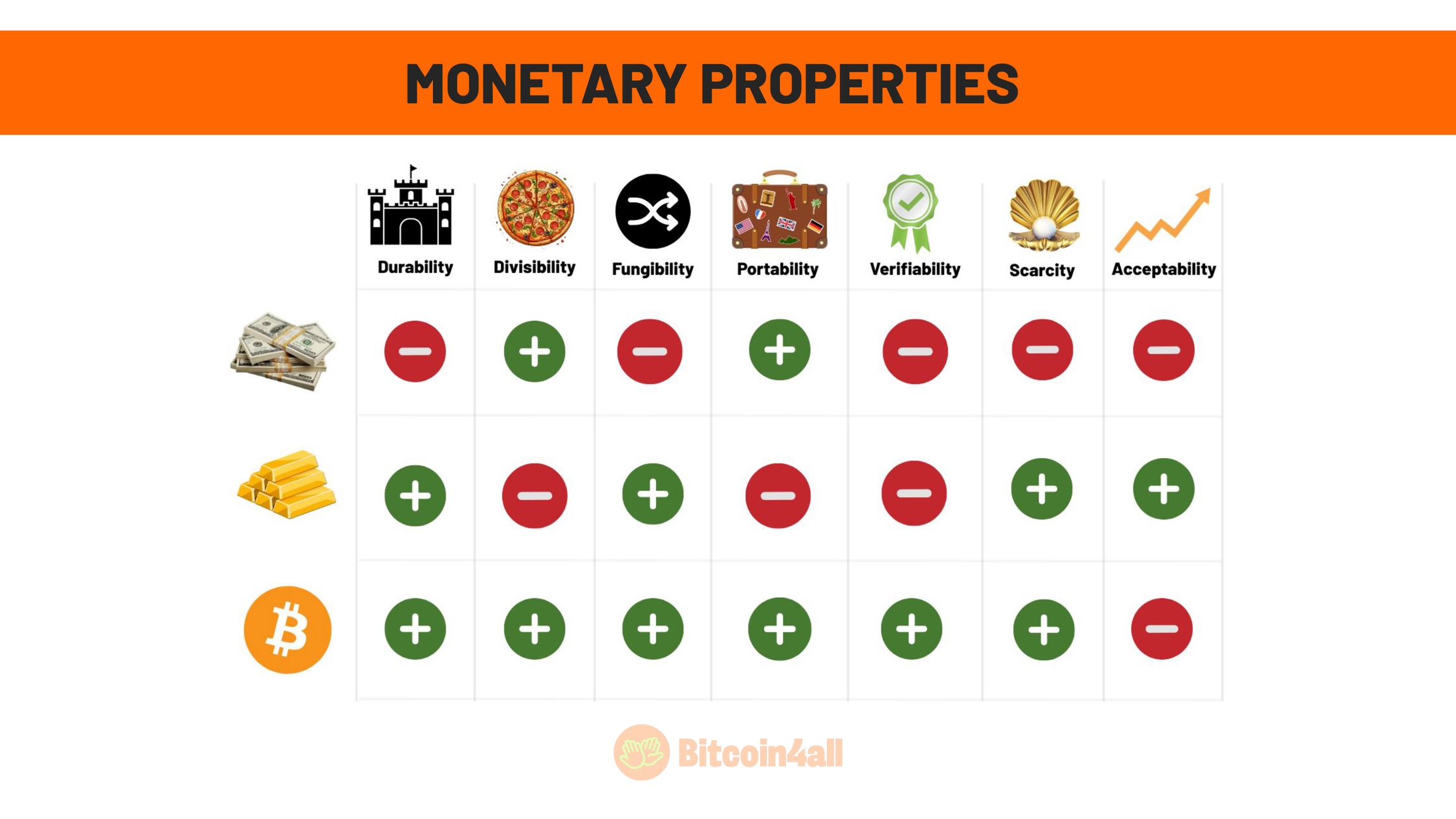
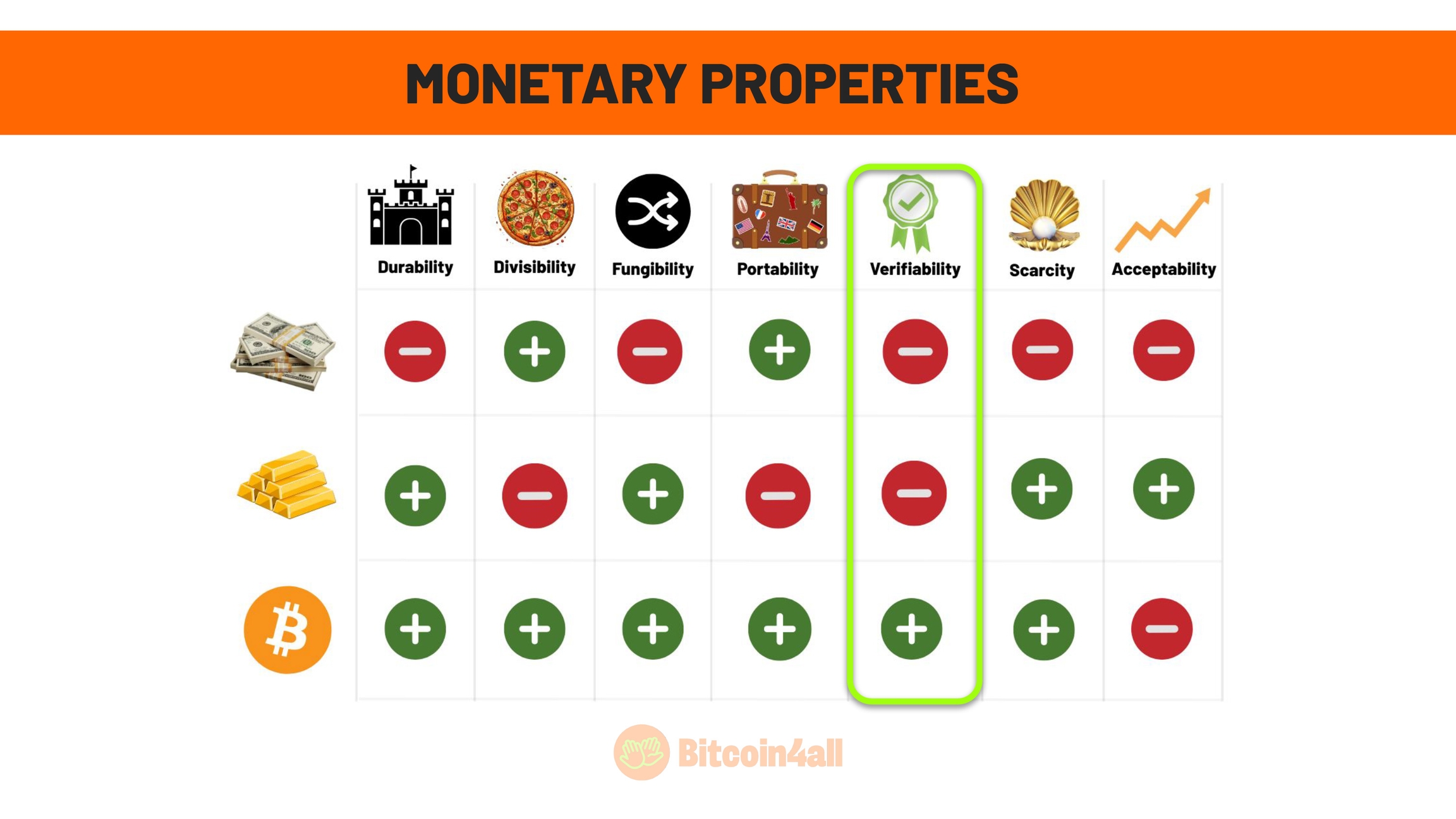
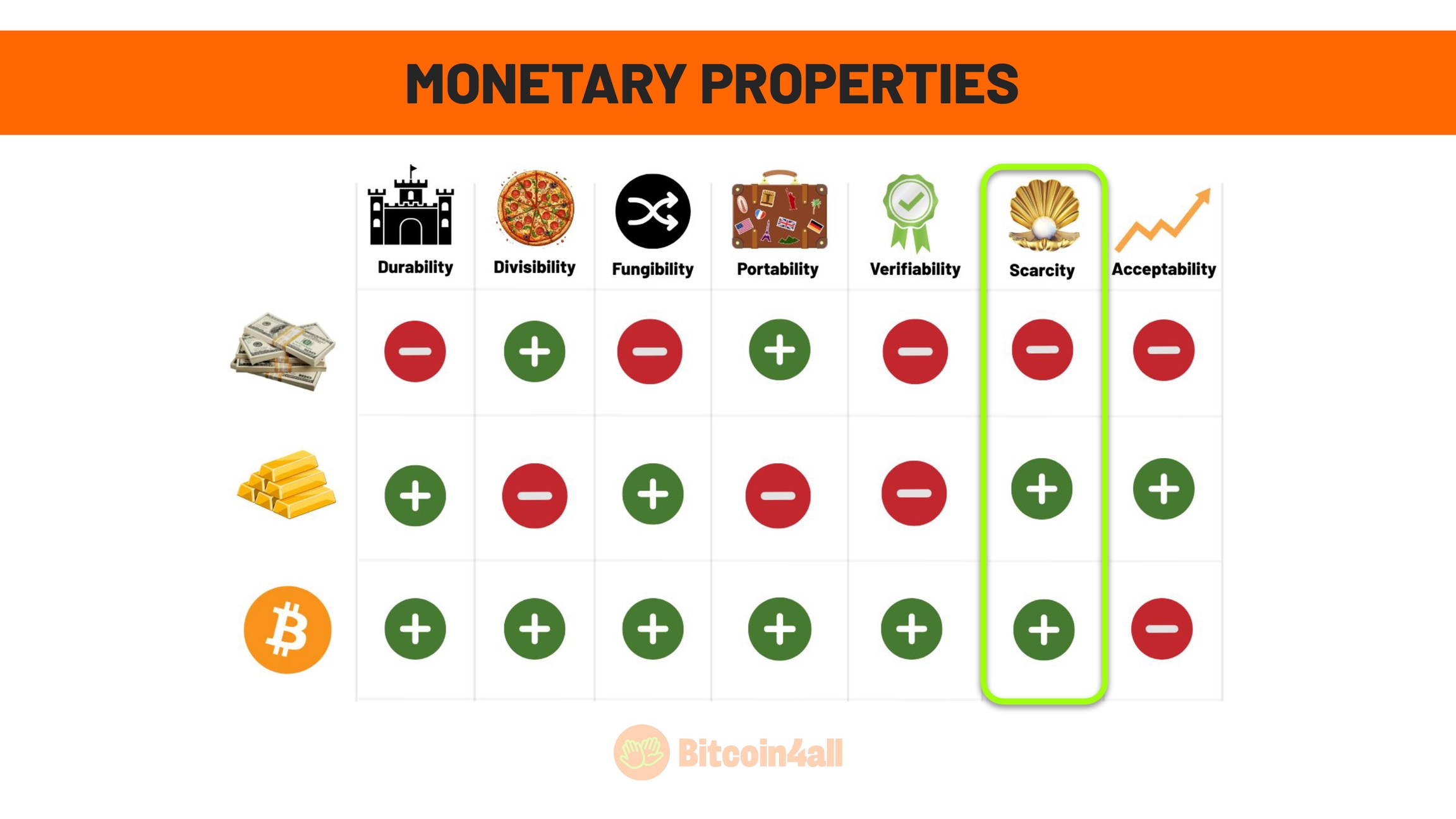
This image shows the main characteristics that define good money, that is, money with strong monetary properties. These characteristics are:
Durability
Divisibility
Fungibility
Portability
Verifiability
Scarcity
Acceptance
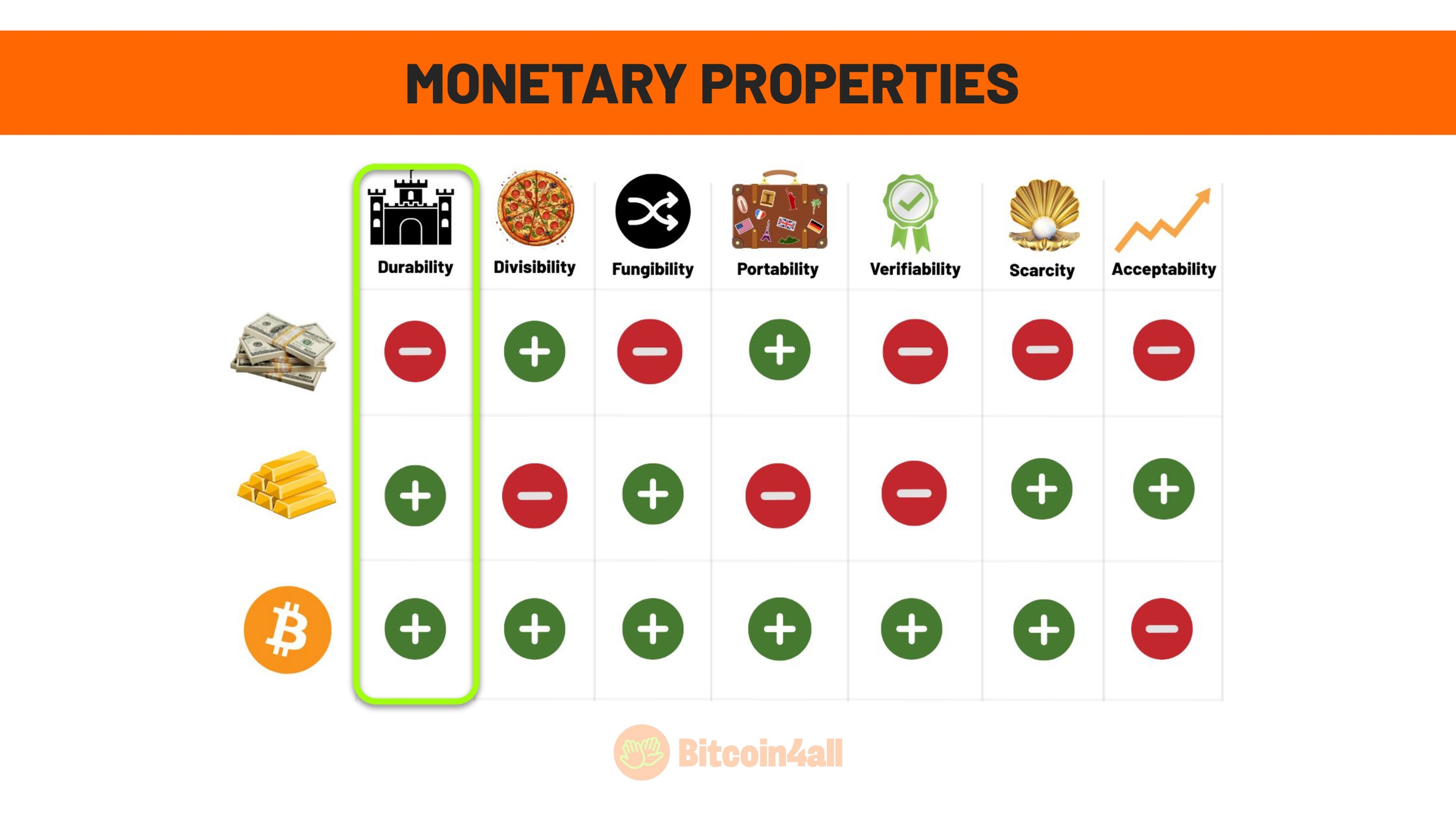
The first feature is durability. Good money must resist wear and the passage of time, guaranteeing its usefulness as a medium of exchange and store of value without deteriorating.
Fiat currencies are non-durable paper money. They can crumple, get wet, tear and deteriorate quickly. Central banks regularly spend millions of dollars replacing damaged banknotes with new ones. Moreover, fiat money as a network depends on central banks that can change the rules of each currency locally. Even if governments create digital currencies, they won't have durable and immutable monetary properties in the long term.
Gold is naturally durable, since it doesn't rust or degrade. On the other hand, because it is a physical asset, it can suffer some wear and tear over time.
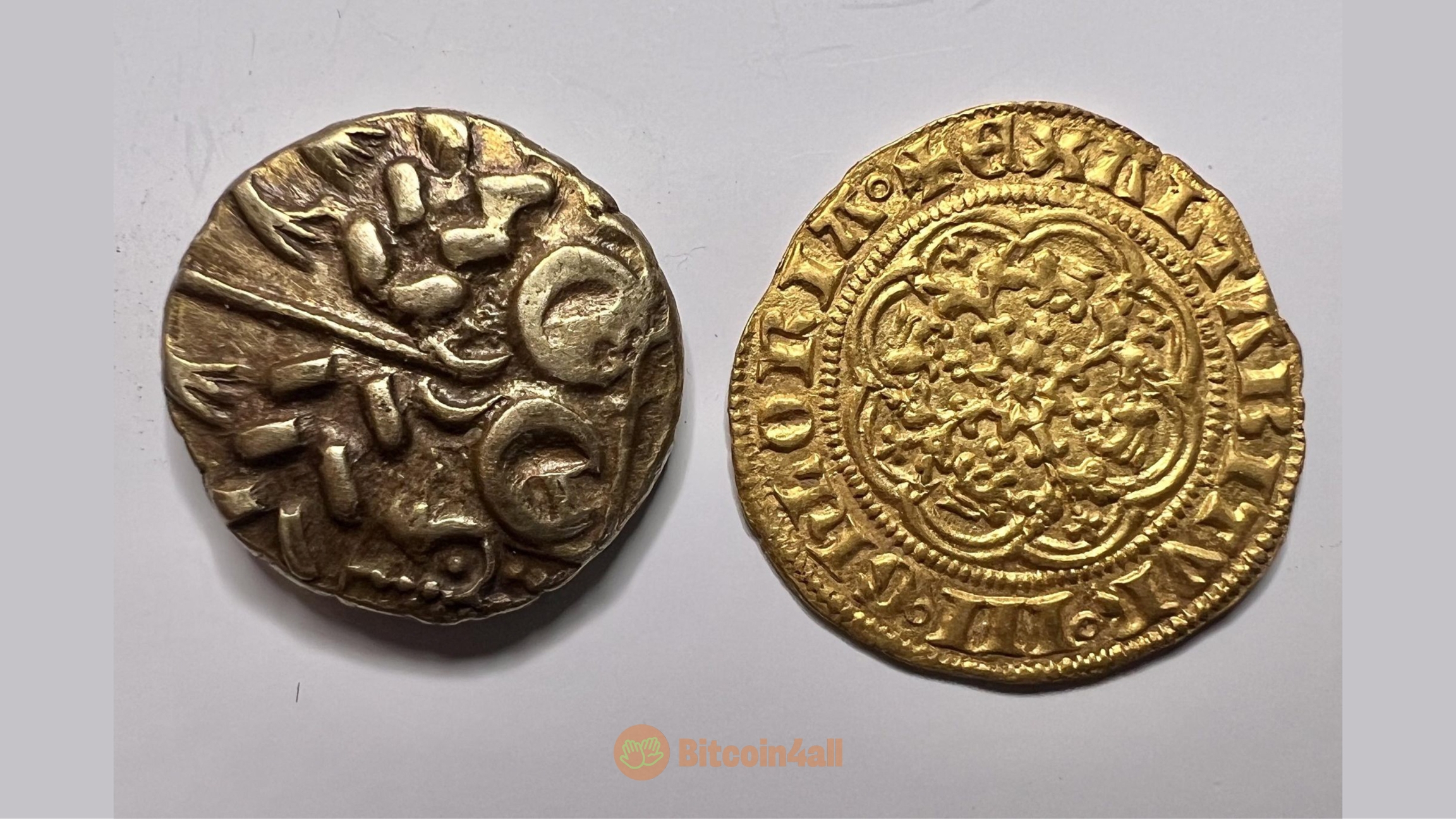

Have you ever noticed how old gold coins have irregular edges? This is because gold coins wear down, which degrades the original value of the coin. It ends up losing the amount of gold that was settled in it.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, is extremely durable because it is digital. There is no physical wear and tear and, as long as there is a node running and processing the network, it continues to exist. In addition, the Bitcoin network is highly resilient. In its 16 years of existence, it has faced constant attacks, but it continues to function uninterruptedly as the most secure and powerful network in terms of computing in the world. That's why Bitcoin is more durable as a currency and resilient as a network than fiat money or gold.
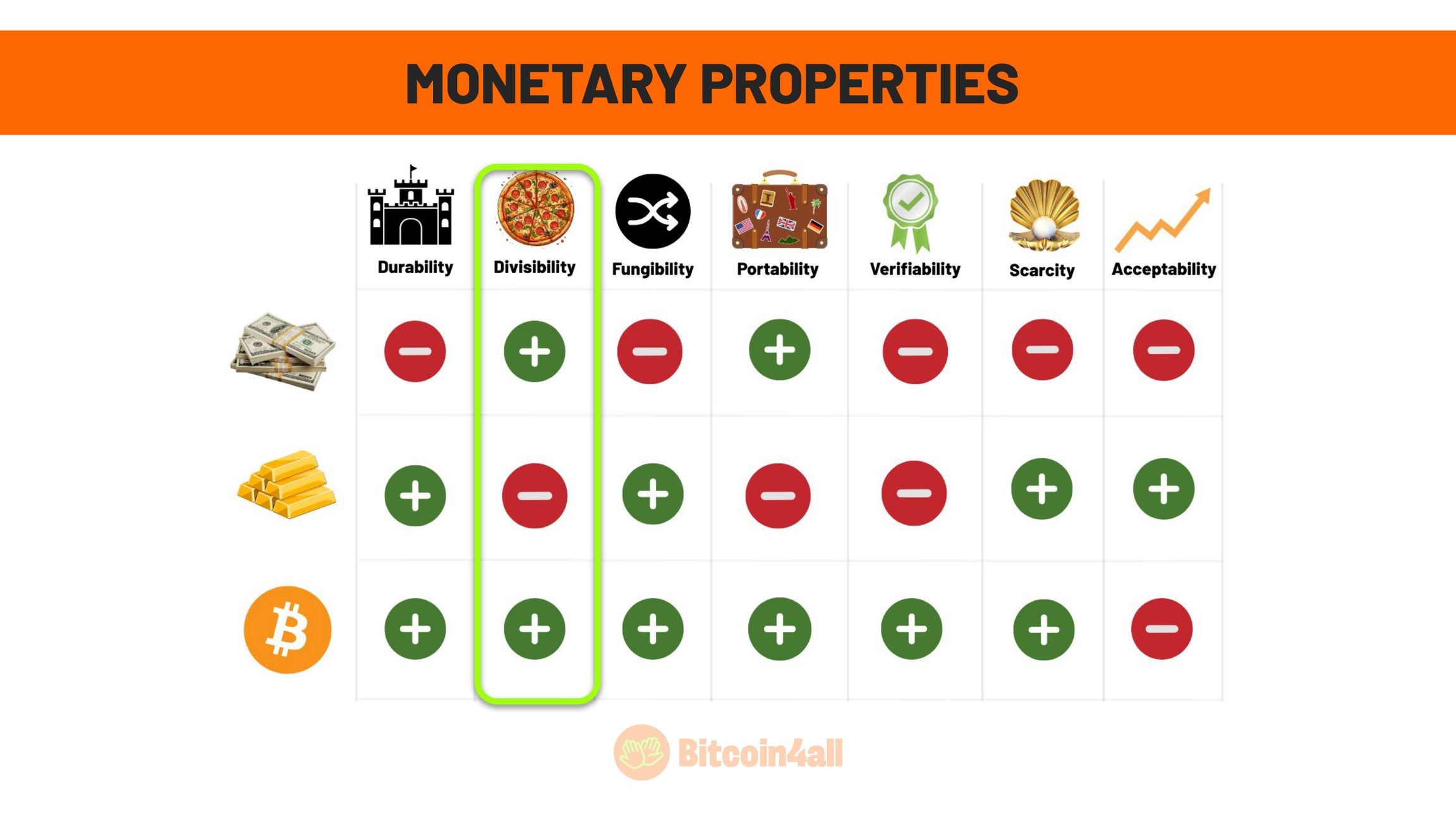
Divisibility is the ability of money to be divided into smaller units, allowing transactions of any value. This is essential to make it easier to use both in major negotiations and in everyday purchases. A practical example: a house cannot be considered money because it is not easily divided into smaller parts. Houses are not money: they are assets or liabilities that are worth an amount of money.
Fiat money is highly divisible and can be broken down into cents, which makes it easier to use in transactions of different amounts.
Gold is divisible into units such as ounces of gold, which allowed it to be used as money in the past. But gold has limitations for microtransactions, which has led to fiat currencies replacing gold as the monetary standard due to their greater divisibility and portability.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, is even more divisible than fiat and can be fractionalized to up to 8 decimal places. Bitcoin's smallest unit is called a satoshi, which allows it to be used for transactions of any value, including microtransactions. This makes Bitcoin an ultra-divisible money. Let's understand how this works.

With the dollar, you need more notes over time because these currencies lose value, right? With Bitcoin, the opposite happens: as it rises in value, you need fewer units to buy the same things. That's why Bitcoin is extremely divisible, it has several decimal places, to make it easier to price goods and services as smaller fractions of it are used.
An entire bitcoin is made up of 100 million satoshis, the satoshi being the smallest unit of a bitcoin. To understand this better, imagine that a bitcoin is like a pizza that can be cut into 100 million slices. When you buy 50, 100 or 1,000 dollars or euros in bitcoin, you're actually buying thousands of satoshis. One satoshi is equivalent to 0.00000001 BTC (seven zeros before the number 1). On the other hand, 1 bitcoin is equal to 100 million satoshis, just as 1 dollar is made up of 100 cents.
Currently, a satoshi is worth less than one cent of a dollar, about a tenth of a cent. In the future, as Bitcoin continues to rise in value and the dollar keeps on losing its value, it is possible that a satoshi will be worth the same as a cent or even a dollar. This reflects Bitcoin's strength as a store of value and medium of exchange. As they absorb value, it becomes easier to price products and services.
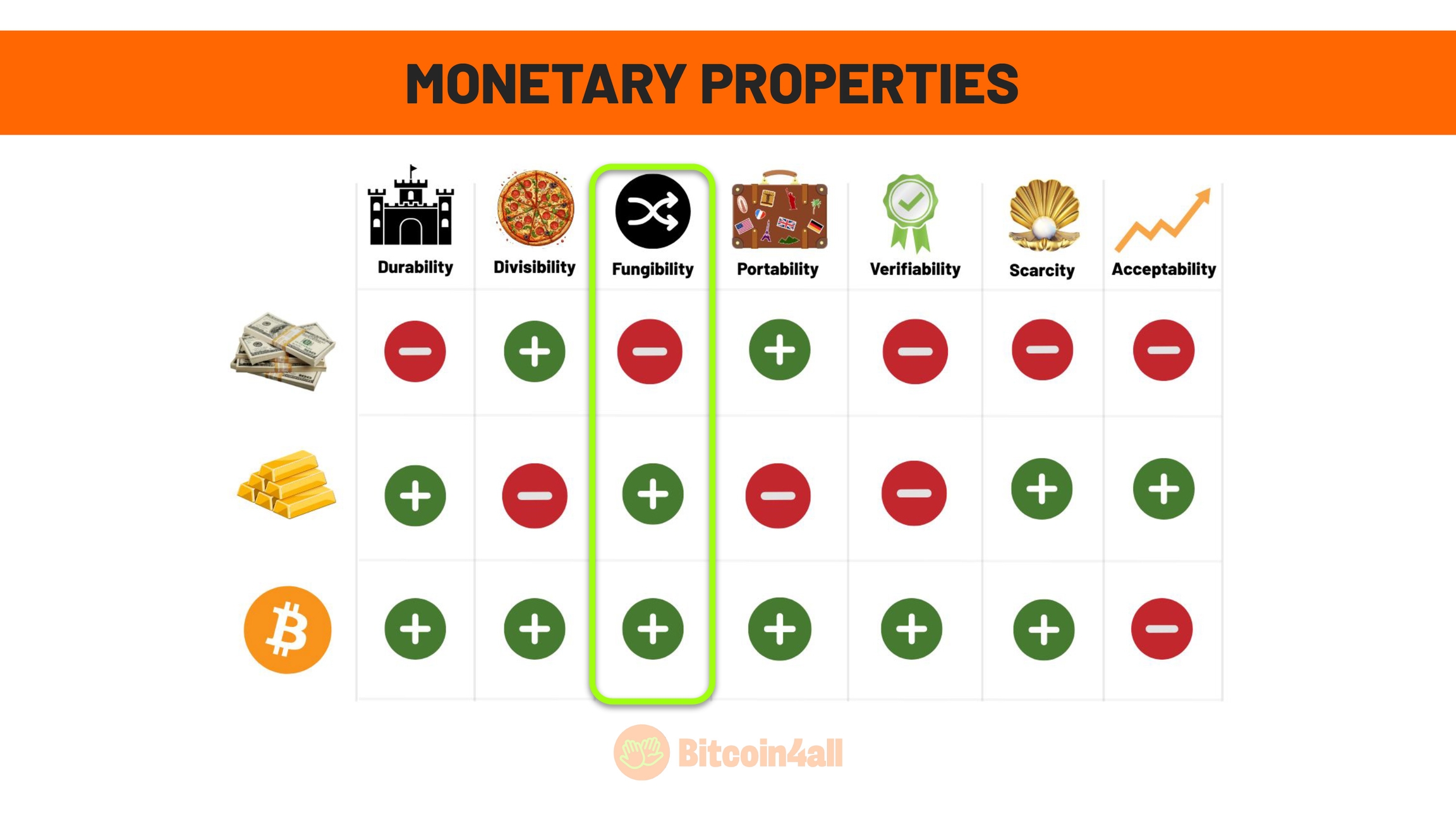
Fungibility is the property of money in which all its units are equivalent and can be exchanged for each other, regardless of their origin or history. It is the property that guarantees that money will be accepted universally, without discrimination between units.
Fiat currencies are not completely fungible. For example, 1 euro is not equal to 1 dollar and the currencies of different countries are not interchangeable. Although within a country a 10-dollar note is the same as another 10-dollar note, that same dollar, for example, is not accepted as legal tender in all countries. Not to mention the differences between rates in countries with high inflation, such as Argentina, which had a "blue dollar" rate and the official government rate, which lacked in value. In times of crisis, fiat currency loses its fungibility.
Gold is highly fungible. An ounce of pure gold is always the same as another ounce of pure gold, regardless of where you are in the world. This makes it more fungible than fiat currencies.
Bitcoin is fungible as well. A bitcoin is the same as any other bitcoin to the network, regardless of where it was traded or its history. This characteristic is essential for its global acceptance as digital money; after all, the Bitcoin network does not discriminate, a bitcoin is always the same as a bitcoin for the network.
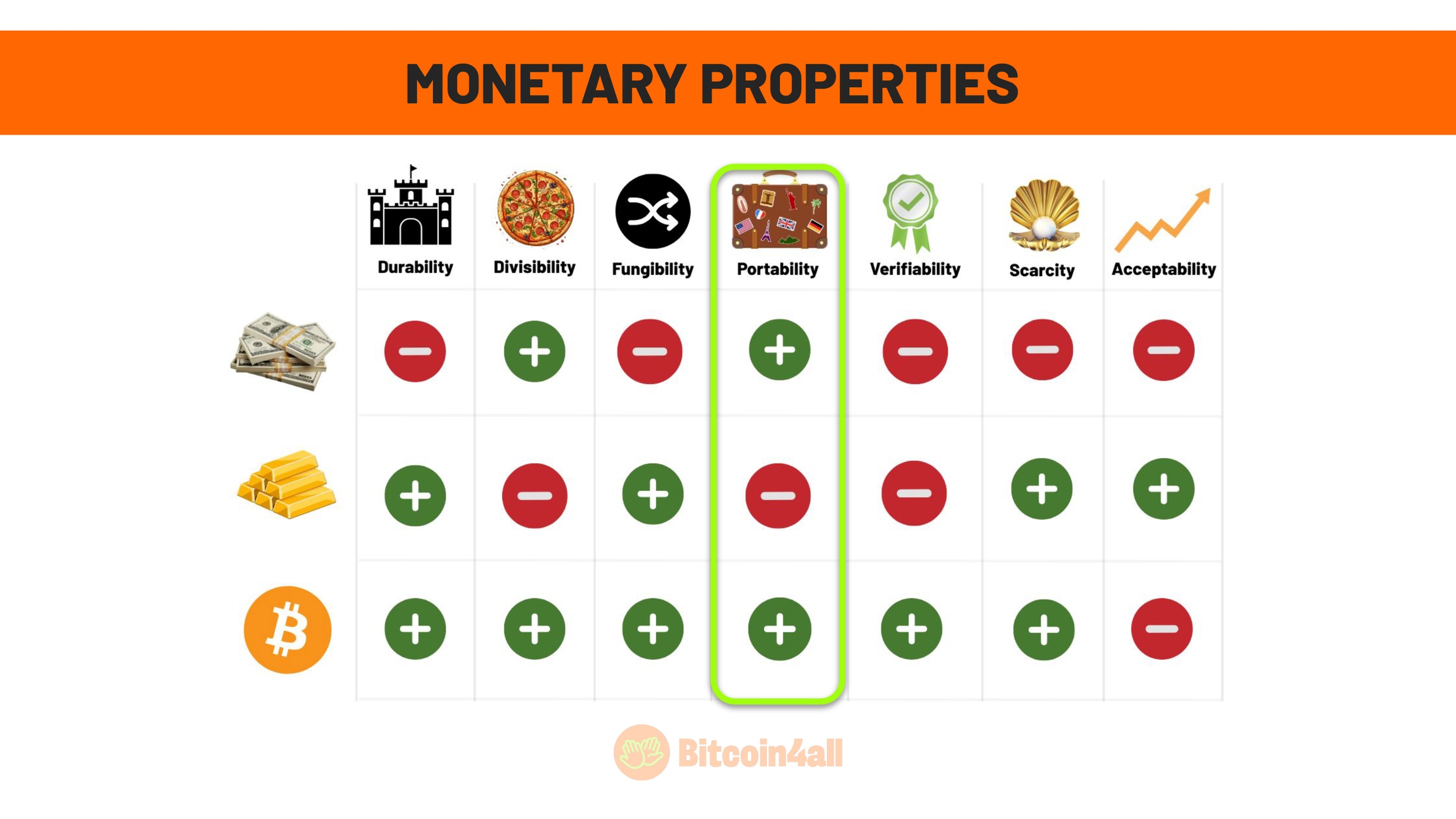
Portability is the ability of money to be easily transported and stored, allowing transactions in different places and situations.
Although coins and small amounts of gold are portable, large volumes, such as millions in gold bars, are heavy and expensive to transport and store. In order to move gold bars between countries, it is common for central banks to melt the bars to verify their authenticity. In addition, transportation involves high logistics and security costs.
Fiat money is more portable than gold. Paper notes or metal coins are light and easy to carry. They are like contracts with an assigned value, represented in physical form. Not to mention the fact that fiat money has become digitized and even more portable.
Bitcoin surpasses them all in this respect. Because it's digital, it doesn't weigh, doesn't take up physical space and can be transported globally in a matter of seconds. Whether it's a small fraction or billions of dollars in bitcoin, transportation is just as fast, secure and absurdly cheaper than any other way of transporting value. It's the most portable form of money ever created. After all, not only is it digital and weightless, it doesn't need anyone's permission to move across borders.

Portability is a major challenge for analog assets such as real estate or commodities. For example, you can't move a plot of land, and even a house could only be transported with great effort in an expensive process, as shown in the image on the left.
With gold, the situation is also complicated. You can't carry it on an airplane without informing third parties that you're carrying this wealth, which compromises privacy, involves bureaucracy and more fees.
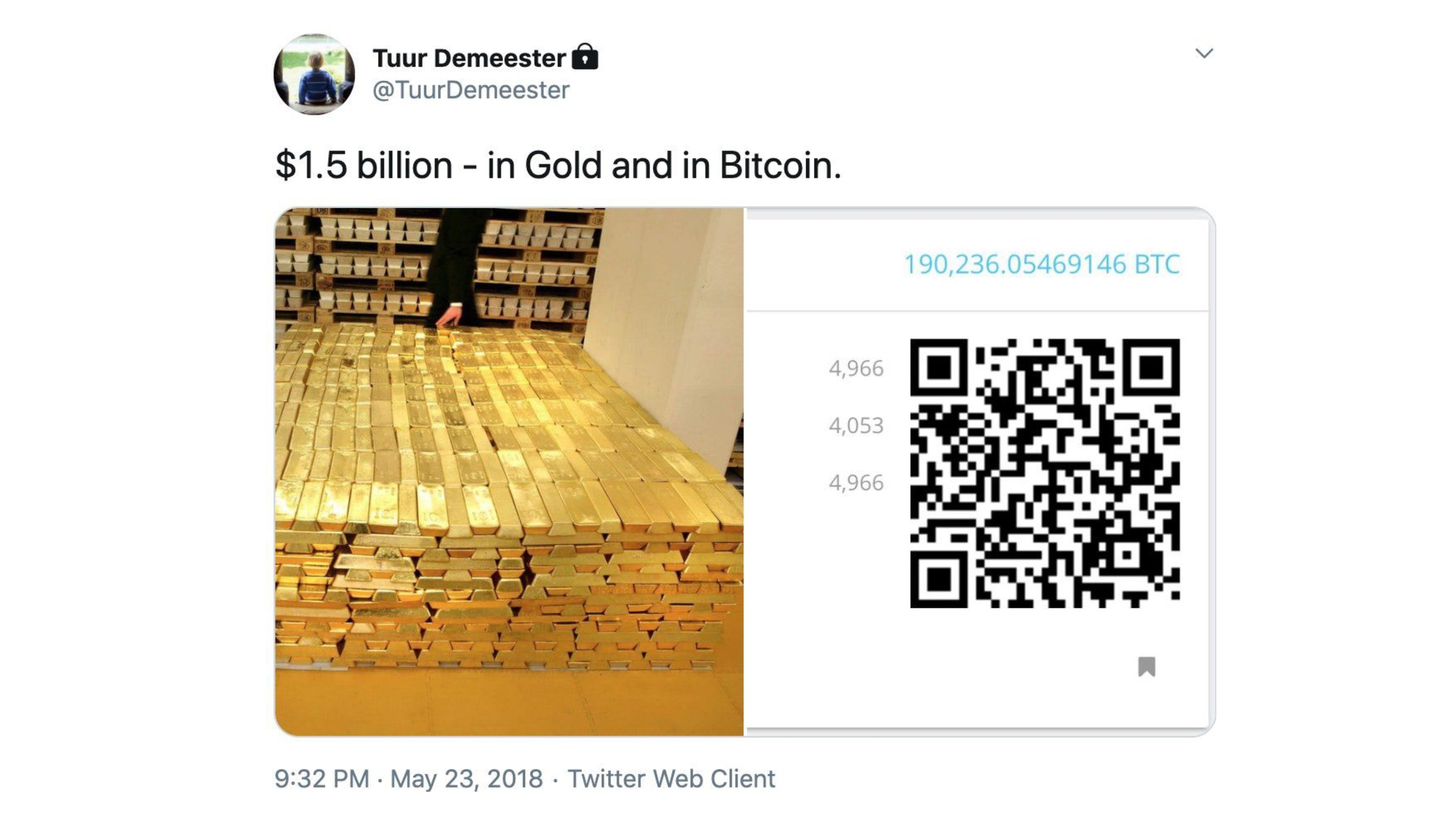
Bitcoin, is unrivaled in portability. Because it is natively digital, it can be transported instantly, without relying on intermediaries or complicated and expensive processes.
This post by Tuur Demeester demonstrates the big difference in portability very well. While $1.5 billion in gold bars takes up an entire room and an expensive security structure, the same $1.5 billion in bitcoin is pure information and fits on a piece of paper or in a few bytes of information. It is the most portable money and/or asset in the world.
Verifiability is the ease with which money can be identified and authenticated as legitimate. This property is essential to prevent fraud and counterfeiting. The simpler and more reliable the verification process, the cheaper and more practical it is to use money as a store of value and a means of exchange.
Fiat money is relatively easy to counterfeit, so much so that fake notes circulate frequently on the market. This forces merchants and consumers to learn basic identification techniques, such as checking for watermarks or security features on banknotes.
In the case of gold, verifiability is even more complex. Practices such as biting into gold to check its authenticity, observing if there was a mark on the metal, were quite common in the past, yet rudimentary. Modern methods, such as chemical or density testing, are still required, which makes the process expensive and time-consuming.
The ease with which you can verify the authenticity of money is essential to guaranteeing trust and efficiency in everyday use.

Even gold can be counterfeited, revealing important limitations in its verifiability. There are many examples of fraud involving gold, such as adulterated gold bars. Even some bars have already been found with tungsten in their core, coated only with a layer of pure gold. Gold-plated coins and jewelry made from low-quality metal alloys are also examples of counterfeiting.
Like we said, verifying the authenticity of gold is expensive and complicated. The process often requires specialized equipment and certificates issued by trusted third parties. This makes the process bureaucratic and difficults gold's use as money, especially on a large scale.
These limitations make gold less efficient in verifiability when compared to Bitcoin, because Bitcoin's authenticity can be proven instantly by anyone using a wallet app or software connected to the network.

Bitcoin is extremely easy and cheap to verify, thanks to its digital and decentralized nature. Unlike other types of money, there is no room for counterfeiting. It is not possible to send or receive "fake bitcoin", because the network validates all transactions before confirming each one. If someone tries to send a "fake transaction", it simply won't be propagated.
The verification is global as well. With a simple command on the computer, anyone can verify the authenticity not only of a single bitcoin, but of all the coins already on the network. This includes the total supply of Bitcoin and the rate at which new coins are issued, guaranteeing absolute transparency of the system as a whole.
This radical transparency is something that has never been offered by any other monetary system in history. All participants have access to the same information about the state of the network, cutting the need to rely on intermediaries or centralized institutions. There is no information asymmetry in the Bitcoin network: the records are public and verifiable by anyone.
Scarcity is the property that defines the difficulty of creating new units of money and is essential for protecting value over time.
Fiat currencies are not scarce. Central banks can print unlimited amounts of money, which often results in inflation, devaluation and loss of purchasing power. This lack of scarcity is one of the main weaknesses of fiat money.
Gold is relatively scarce because its extraction depends on physical processes and limited resources on Earth. But even so, the discovery of new deposits or technological advances can increase the supply of gold over time, which reduces predictability and scarcity compared to Bitcoin.
Scarcity is a crucial factor in determining a money's resistance to inflation and its ability to preserve value.

Although it is extremely difficult and expensive to produce gold in a laboratory, the global supply of gold continues to grow due to the constant discovery of new deposits. Advances in mining and technology allow gold to be extracted in previously inaccessible locations, gradually increasing the amount of gold available on the market.
This unpredictability in the supply of gold means that it is not absolutely scarce. This differentiates gold from Bitcoin, which has its supply fixed and known from the start, being even more predictable as a store of value.

In addition to terrestrial deposits, new frontiers for gold mining are being explored, such as asteroid mining and ocean mining. These futuristic technologies aim to extract resources from places that were previously inaccessible.
Some asteroids contain large quantities of precious metals, including gold. Space companies are already developing technologies to exploit these resources in the future. The deep sea is also a potential source of gold and other valuable metals and there are already projects underway to make it possible to extract these submerged deposits.
Although these technologies are still in their early stages, they represent the possibility of significantly expanding the supply of gold in the future and constantly reducing scarcity.
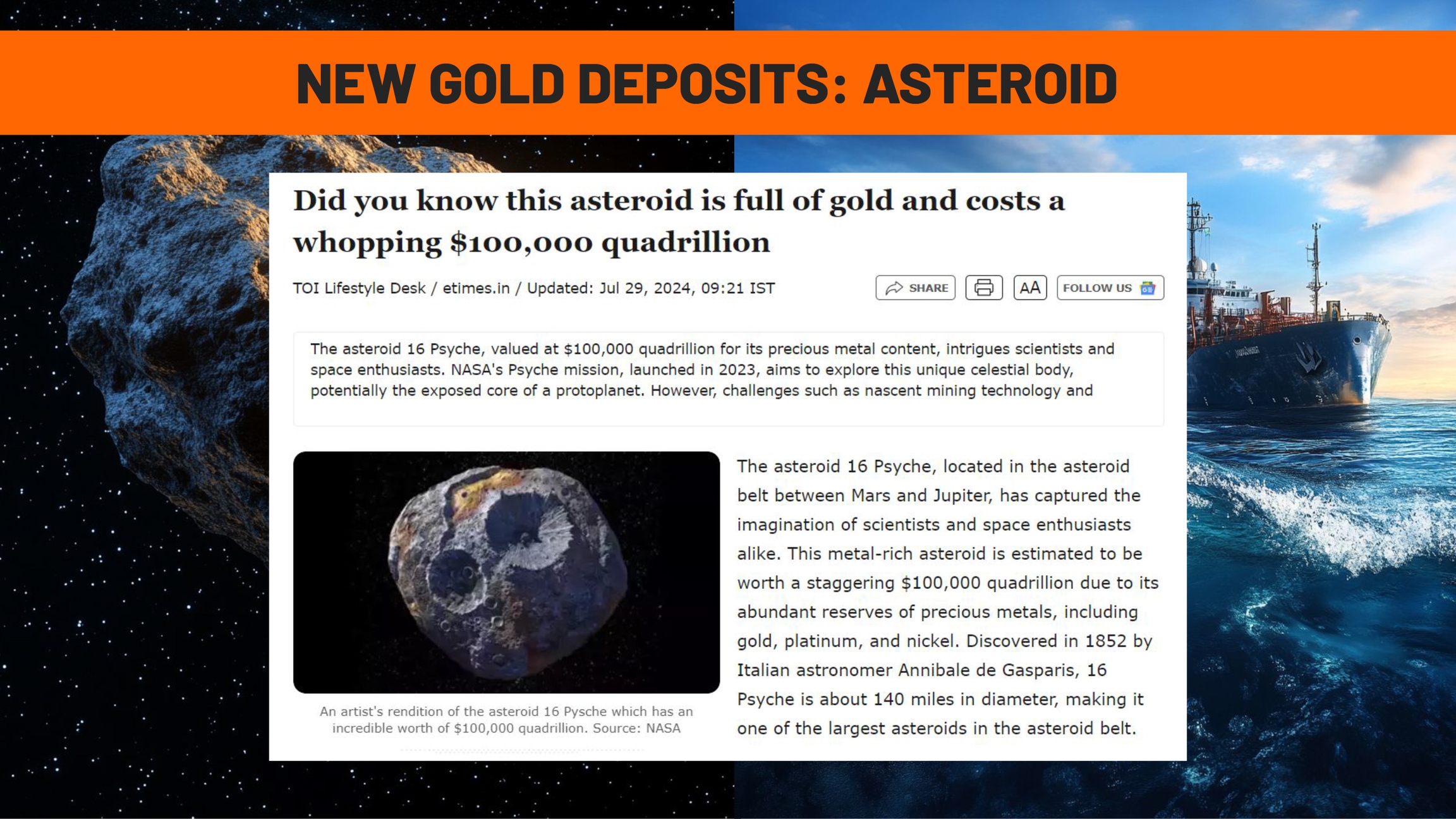
Reports like this show that there are asteroids full of precious metals, including gold, worth an estimated 100,000 quadrillion dollars. If space mining becomes viable, it could completely eliminate the scarcity of gold, one of its main monetary properties.
If gold became abundant, it would lose its ability to act as a reliable store of value. In this scenario, its use would be limited to more specific functions, such as in jewelry making, where its shine and beauty continue to be valued, or in industrial applications, such as in the production of electronic chips, thanks to its excellent conductivity.

Ocean mining is becoming another major technological frontier, with countries such as Norway already exploring the feasibility of extracting gold and other precious metals from the seabed. However, this type of mining is generating intense debate with environmentalists, who warn of the ecological impacts of this activity.
Although ocean mining faces technical and ethical challenges, it is likely that, over time, technological advances will make these operations viable. This scenario reinforces the fragility of gold as a long-term store of value as technology advances.

Unlike gold, Bitcoin does not depend on external factors to maintain scarcity. The maximum supply of 21 million units is fixed and programmed from the start. No technological innovation or future discovery can increase the supply of Bitcoin without consensus in the network.
This means that Bitcoin is mathematically scarce. This equation reflects how the supply of Bitcoin is calculated and how it tends to become increasingly limited over time. In the next lesson on halvings you will understand this equation in detail, but the main point is that Bitcoin is absolutely scarce, while other types of money, commodities or assets are only relatively scarce.
The scarcity of gold is based on statistical estimates and limited data, subject to change with the discovery of new deposits or advances in mining. This inevitably increases the supply of gold over time. Fiat money, on the other hand, can be printed indefinitely by central banks, eliminating any notion of scarcity.
In the case of Bitcoin, the supply is unchanged. It is possible to accurately predict, decades in advance, how the issuance of new bitcoin will take place, something that no traditional currency or asset can offer. This transparency and secular predictability make Bitcoin much more reliable and stable as a store of value.
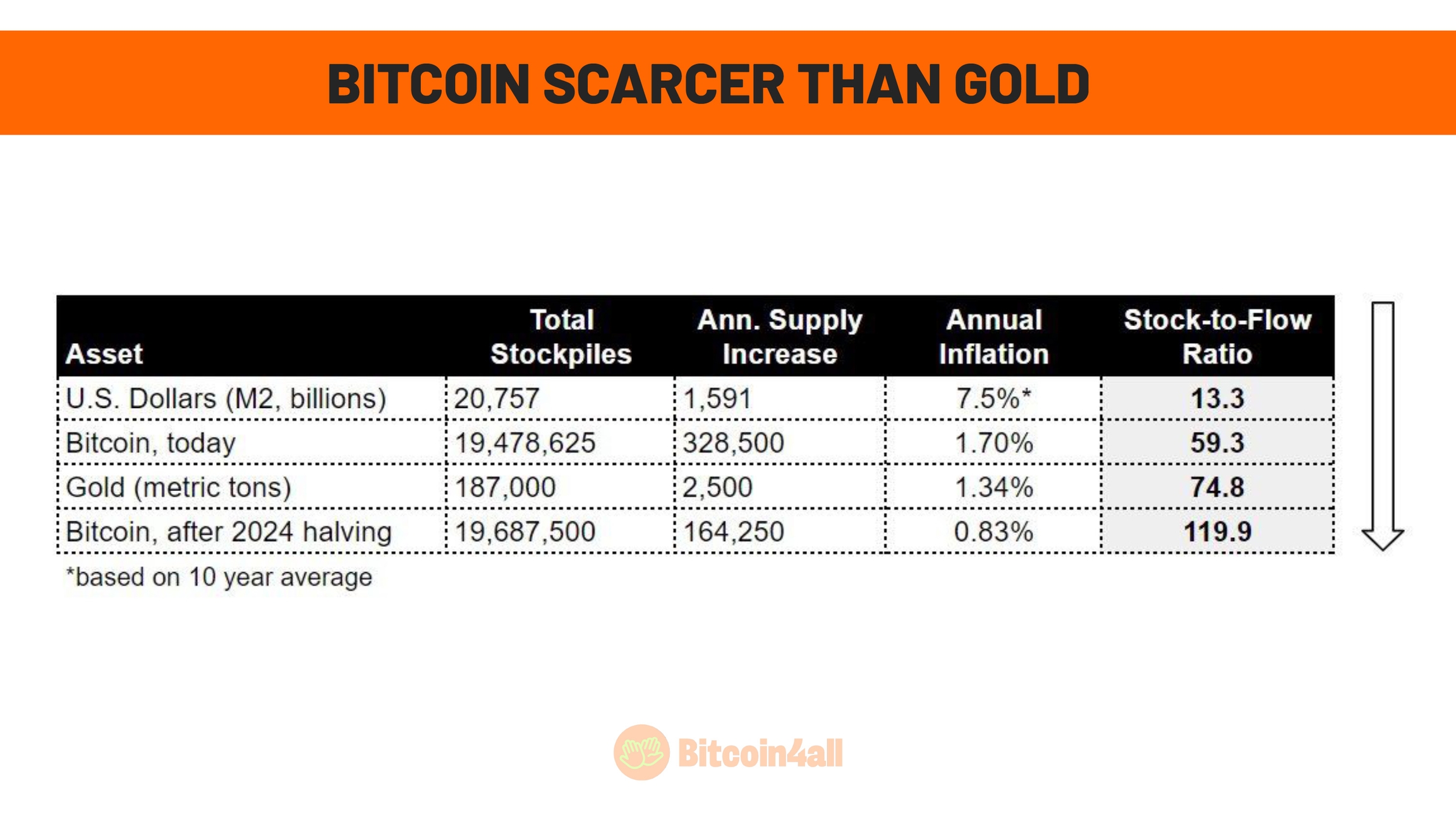
By 2024, Bitcoin officially became scarcer than gold, according to the stock-to-flow (S2F) metric. This metric is used to measure the scarcity of an asset by calculating the ratio between the total stock available (stock) and the quantity produced annually (flow). Assets with a high S2F, such as gold and Bitcoin, have a limited supply, which makes them more valuable because they are more difficult to create new units of.
In the case of gold, its relative scarcity is linked to its annual production, which depends on factors such as land mining and the possibility of ocean or space mining in the future. Bitcoin, on the other hand, is programmed to become increasingly scarce over time, thanks to halvings, which halve the issuance of new bitcoins every four years. This process ensures that, over the years, the supply of new bitcoin decreases dramatically, increasing the stock-to-flow ratio.
Bitcoin's high S2F suggests that it has enormous potential to continue appreciating as demand for a truly scarce asset increases.
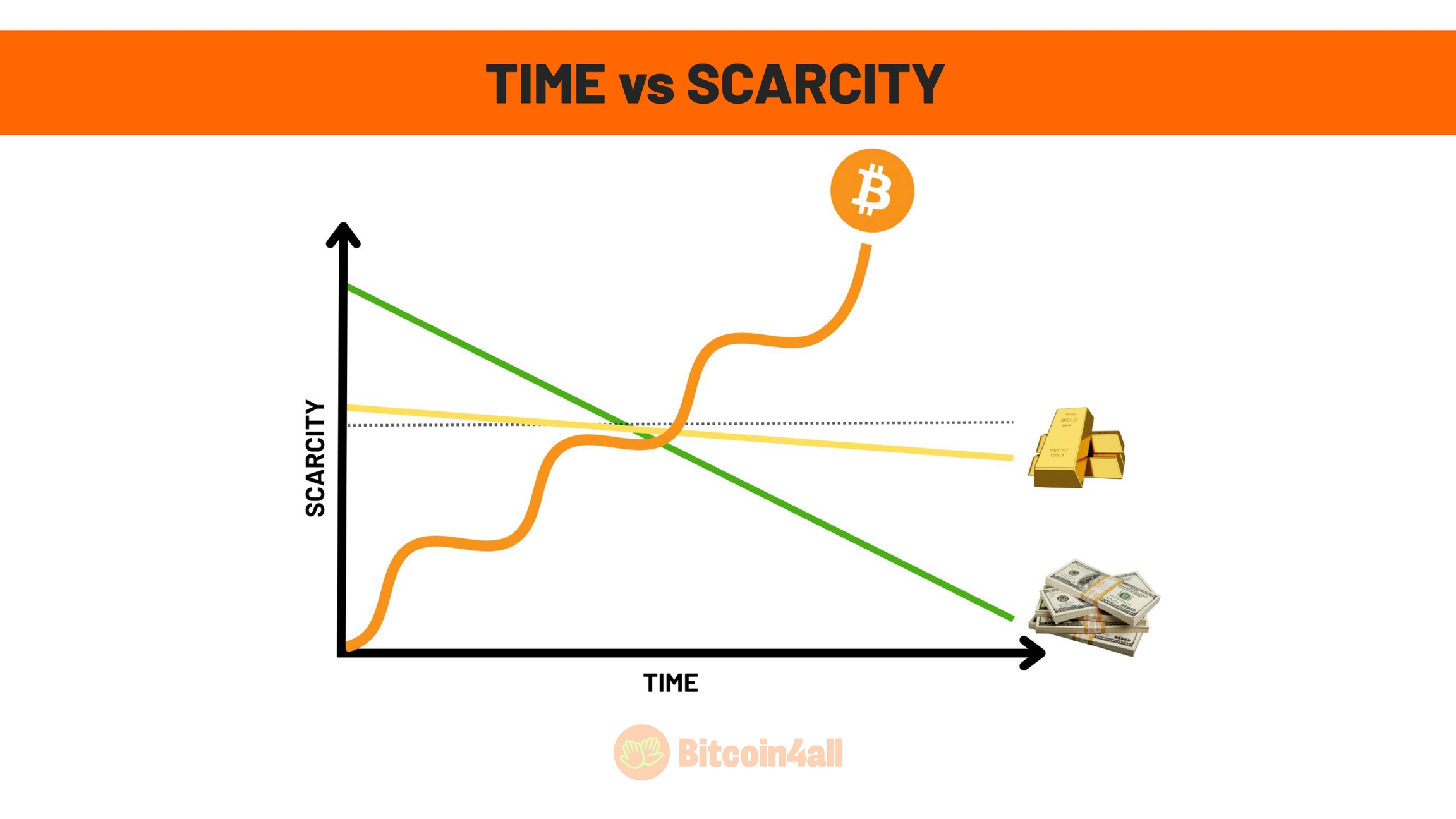
In short, Bitcoin's scarcity tends to increase over time, while gold and other assets tend to become less scarce. Fiat money, on the other hand, is not at all scarce, which is why it has melted in value in all countries under the current fiat standard.
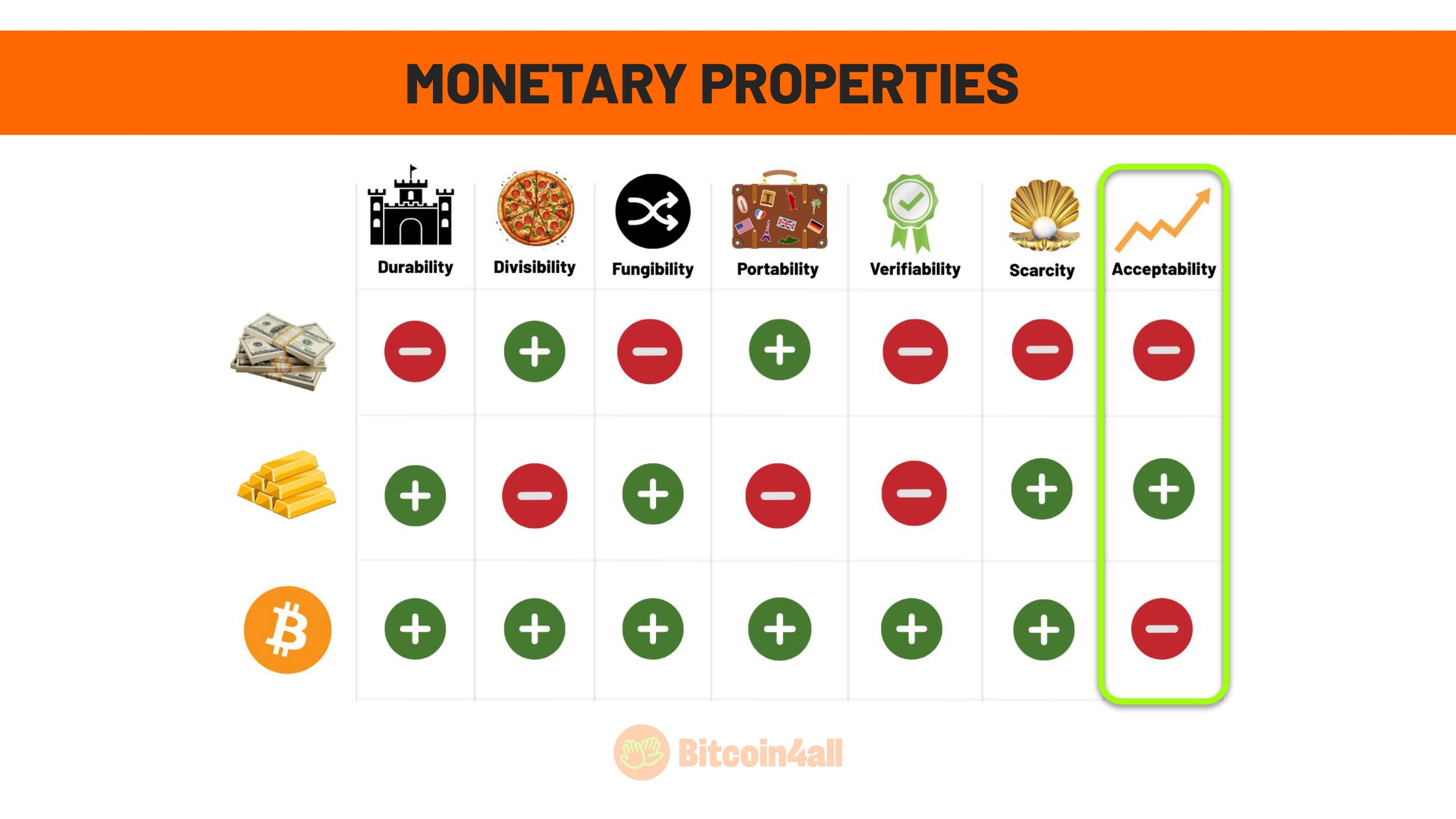
The last monetary property is acceptance, which measures the level of adoption and the extent to which people recognize something as money. In the case of fiat currencies, acceptance is limited. Each country has its own currency, which is not always recognized or accepted outside its borders. This creates barriers in international transactions, making it difficult for money to be universal.
Gold has been widely accepted in the past and has established itself as solid money throughout history. To this day, gold is recognized globally as a store of value, even though its use as a means of exchange has diminished with the emergence of fiat currencies.
Bitcoin is still in the process of being accepted. It is not widely recognized as money or a store of value by all people, companies and countries. But this scenario is changing. In recent years, governments, large companies and investors have begun to adopt Bitcoin and recognize it as a legitimate form of digital asset or money. Although it's not yet a global unanimity, that doesn't mean it never will be.
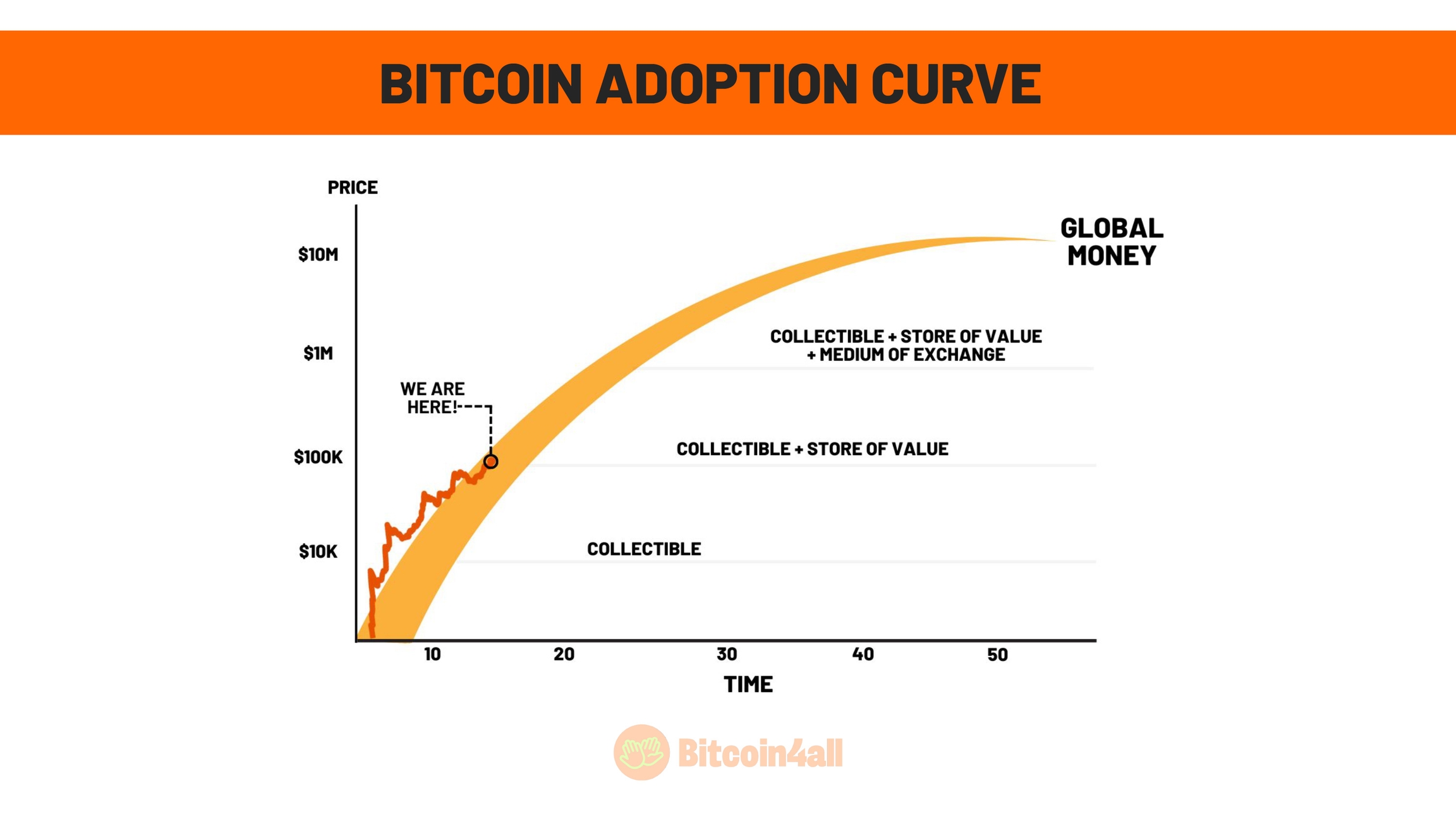
Bitcoin has made significant progress on the adoption curve. The Lindy curve is a good illustration of the stages money goes through until it becomes a global standard. This model explains how Bitcoin is evolving:
In the beginning, money was born as a collectible, something that few people value or accumulate out of curiosity or foresight.
Over time, it has established itself as a store of value and is recognized as a reliable way of preserving wealth.
The following stage is when Bitcoin is used as a medium of exchange, facilitating everyday transactions.
The final stage comes when people start pricing goods and services directly in Bitcoin, indicating that it has become a global monetary standard.
This graph shows that although Bitcoin is still far from being a global standard, it has already made considerable progress. The recent milestone of reaching 100,000 dollars is a reflection of its growing acceptance as a store of value. Governments and institutions around the world are beginning to recognize its potential.
The crucial point is that we are still at an early stage of this technological and monetary revolution. The great opportunity of the century is the possibility of accumulating and getting involved with Bitcoin now, while its global adoption is only just beginning.
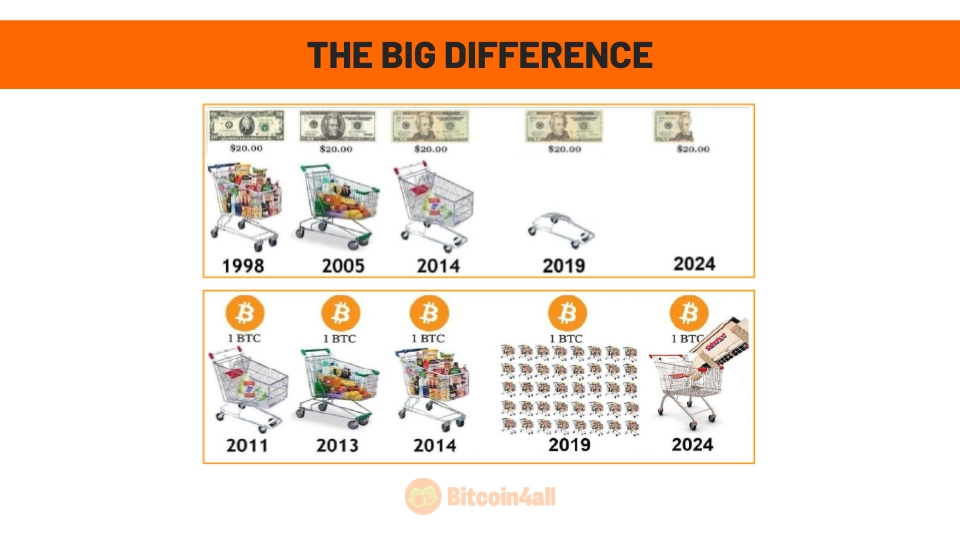
Bitcoin is a superior form of money because its purchasing power increases over time, while the opposite happens with fiat money. With fiat currencies, such as the dollar, the euro or pesos, the value constantly decreases due to inflation and money printing. This means that the same banknotes buy fewer and fewer goods and services over the years. They lose their function as money.
Bitcoin follows the opposite path. Its limited and programmed supply of 21 million units means that, as adoption grows and demand increases, its value and purchasing power will also increase. Historically, those who have kept Bitcoin have seen their purchasing power grow, unlike those who have kept their savings in fiat currencies, which continually lose value. Bitcoin is gaining function as money.
This difference reflects one of Bitcoin's main advantages: it is money designed to appreciate and protect the purchasing power of its users over time, something that fiat money, due to its inflationary nature, has never been able to offer.
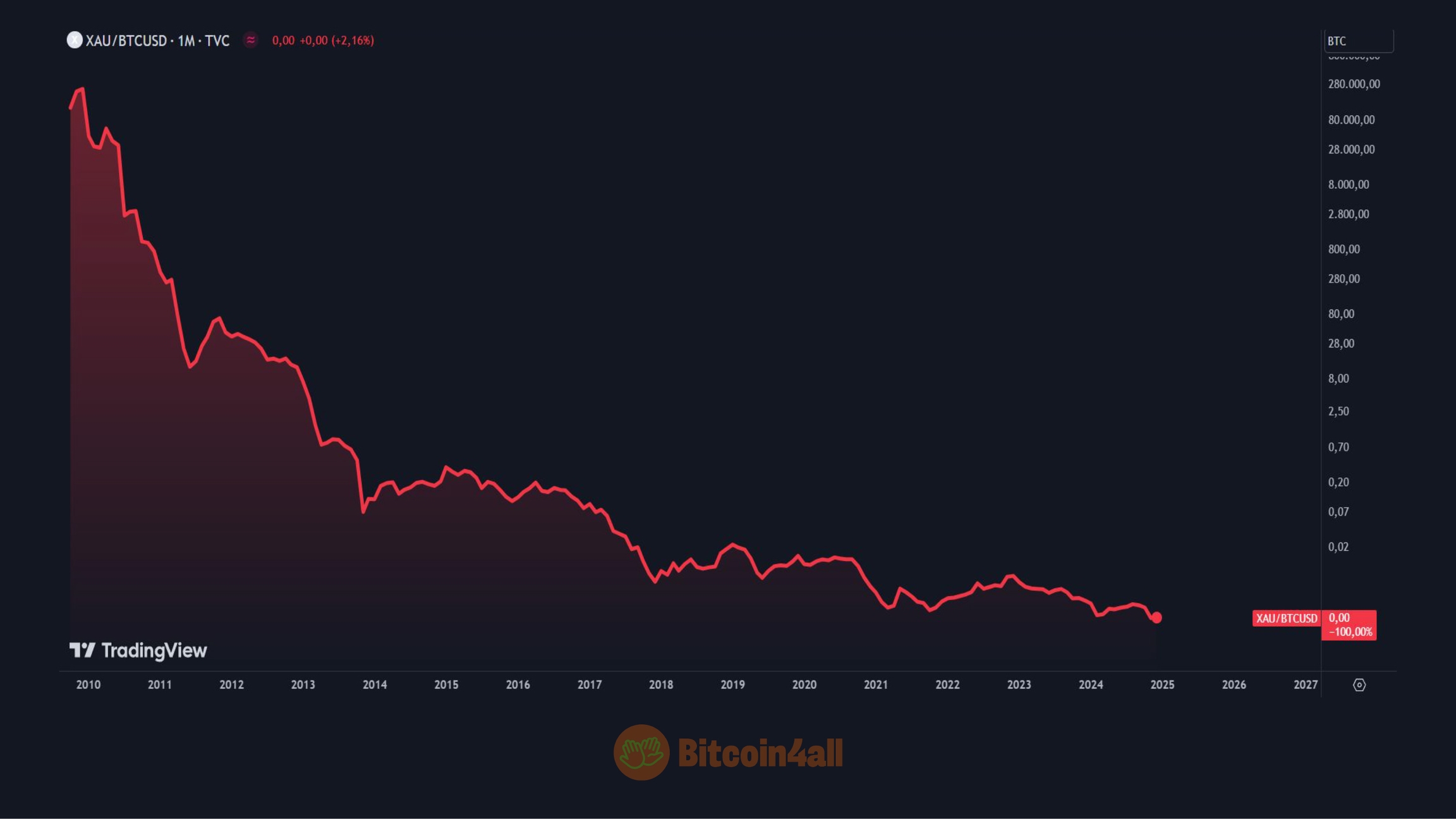
Gold itself is gradually being demonetized by Bitcoin. When priced in bitcoin, gold has lost almost 100% of its value. This shows us how Bitcoin is replacing gold as the world's oldest store of value.
But Bitcoin goes further, being not only an evolution of gold as a store of value but also a superior form of money, since it has much better monetary properties than gold. While gold faces limitations such as portability, divisibility and verifiability, Bitcoin overcomes all these barriers with its digital nature, programmed absolute scarcity and ease of transfer and store. Bitcoin is better money.

Another important point of this lesson is that Bitcoin is better money because it is fairer money.

Fiat money suffers from a phenomenon called the Cantillon Effect, described by Richard Cantillon in 1730 in the book "The Cantillon Effect". This concept illustrates how those closest to the source of the new money benefit disproportionately, while those furthest away suffer more.
In the past, the creation of new money was controlled by kings, who distributed the money first to dukes, nobles and other close allies. These "friends of the king" used the new money to acquire goods and assets such as horses, houses and gold. As the newly created money circulated through the economy, it led to price rises. By the time it finally reached the hands of ordinary people, the poorest, purchasing power had been deeply eroded. And so the people at the end of the circulation chain were always the ones who suffered the most. The money that reached them was already devalued and its real value was much lower.
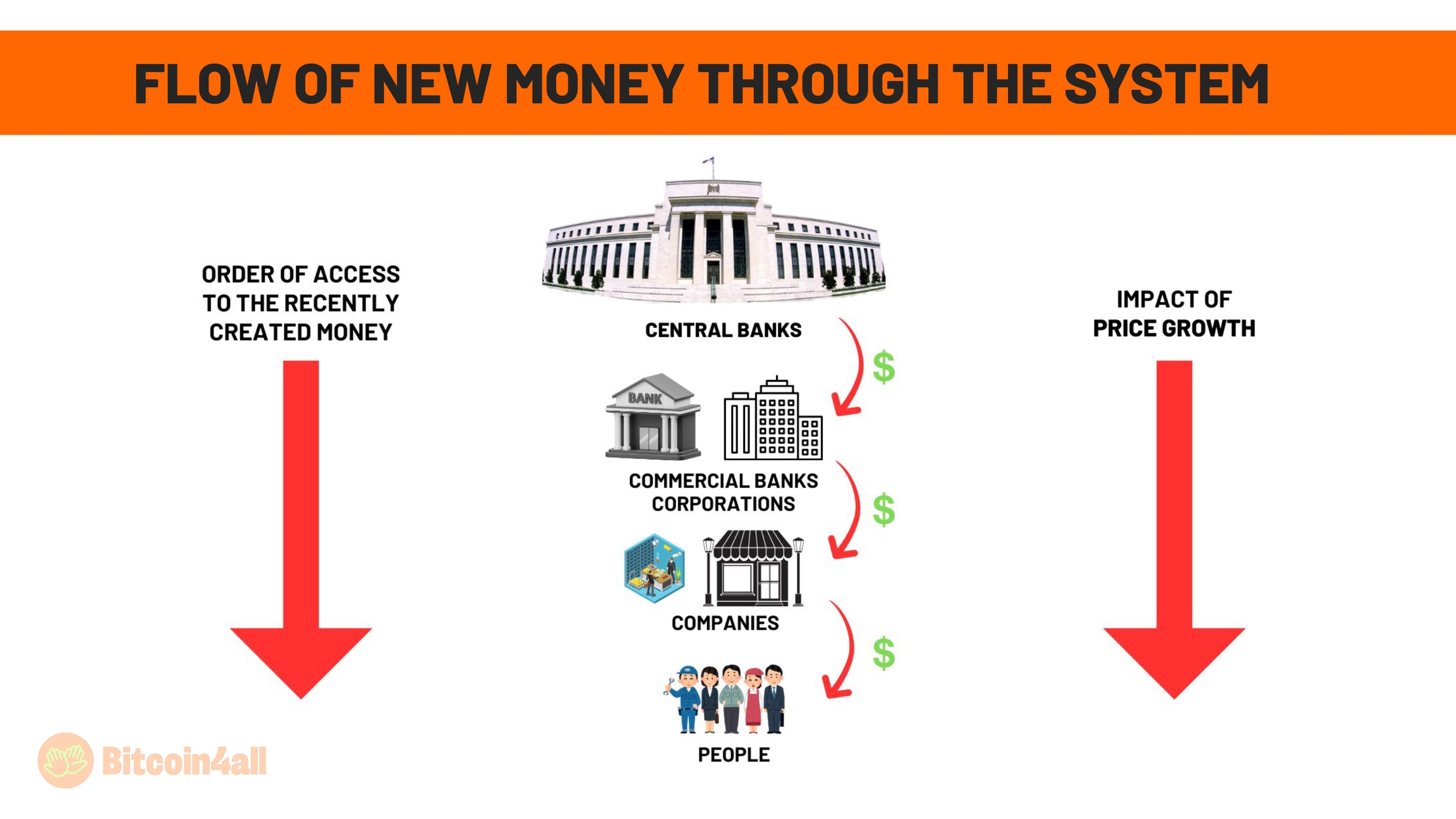
In the modern world, money still follows the same flow as in the days of kings, but with updated characters. Now, central banks create money and the first to receive it are the big banks and corporations. These institutions use the newly created money to invest in or repurchase their own assets, such as shares and stocks. The money is then used to pay executives, directors and other senior staff. Finally, it reaches the employees and customers of the economic base.
This flow explains why those who receive the money first are better able to protect their purchasing power: they have access to the money before prices rise. On the other hand, those at the end of the queue, usually the poorest people, suffer the consequences. When the money finally reaches them, the prices of goods, services and assets have already risen, making everything more expensive and unaffordable.
The Cantillon Effect exposes this unfair dynamic. The closer you are to the "money printer", the more you benefit from it and suffer less from the dilution and devaluation caused by newly created money. Meanwhile, the poorest people suffer the most. They receive money that is already devalued and face high prices, even on assets that could protect them, such as real estate or other investments. These assets have already had an injection of capital in the previous stages, becoming even more expensive and inaccessible to those at the end of the queue for new money.
This effect is perverse because it traps people in a vicious cycle of devaluation and impoverishment. Many feel that they work tirelessly but fail to accumulate wealth as the value of their earnings is constantly eroded. This explains why the biggest cause of poverty and inequality in the world today is related to the way central banks and governments deal with money and their monetary policies.
These same central banks and governments have the exclusive power to print money and unleash this cascade of events, which benefits banks and fiat corporations and penalizes the majority of the population, perpetuating the economic abyss.
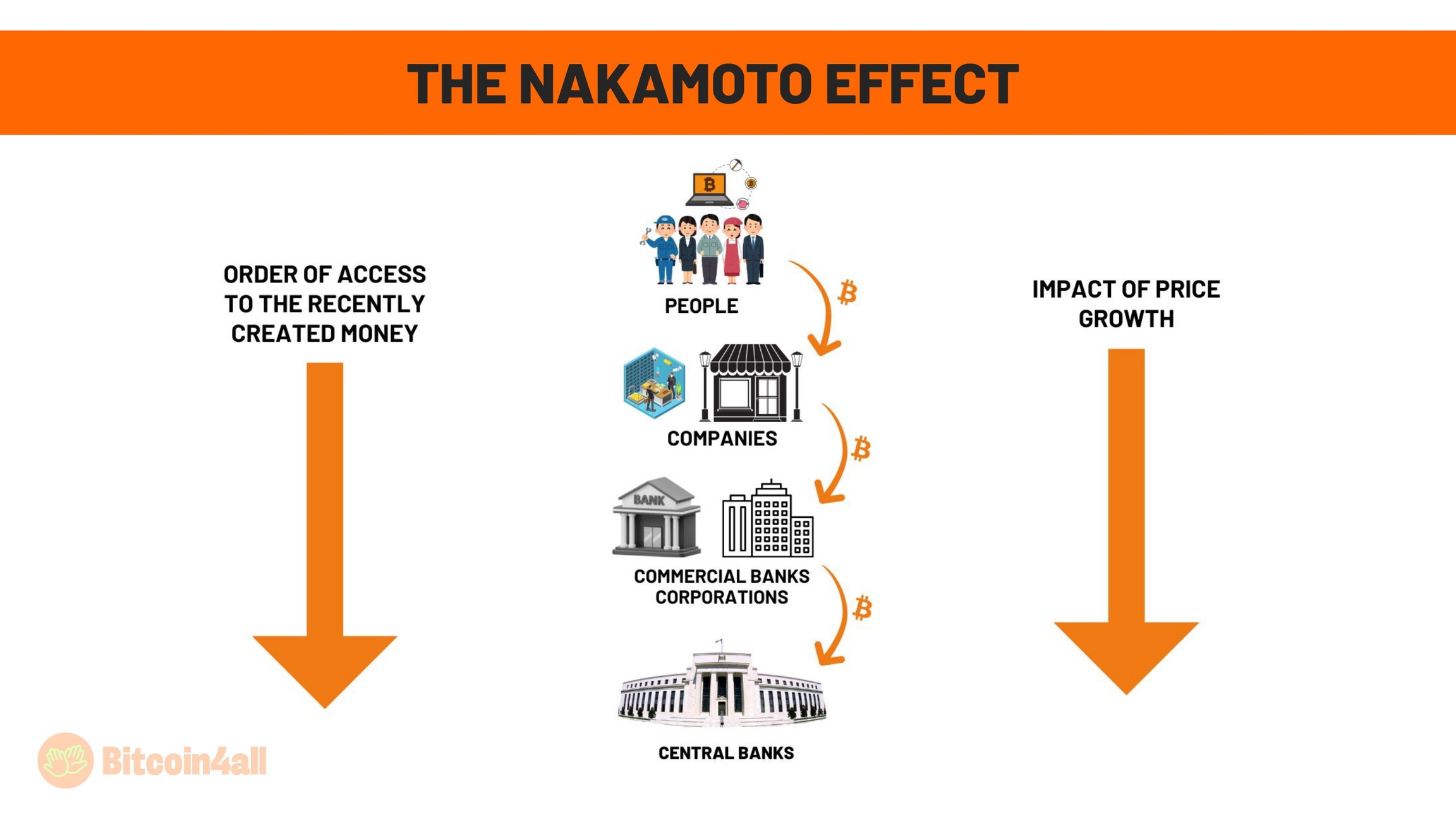
Bitcoin reverses the Cantillon Effect because it does not depend on the printers controlled by governments or central banks. There's no way to print more bitcoin and dilute the circulating supply. Inverting the usual fiat logic, it ends up generating more value for those furthest from the printing presses: first for ordinary people, who began to accumulate bitcoin individually, then for companies, later for banks and corporations and, only recently, for governments, which are beginning to recognize the importance and are finally "giving in" to Bitcoin.
This dynamic is revolutionary because it redistributes economic power organically. As Bitcoin appreciates in value, it offers an alternative to the traditional system, freeing people from the vicious cycle of devaluing fiat currencies, the so-called "rat wheel", where people work tirelessly just to maintain purchasing power in a system supported by inflationary theft.
By accumulating Bitcoin, people become less dependent on money controlled by governments and central banks. Bitcoin represents a way of preserving wealth that empowers individuals and not the cantillionaires benefiting from proximity to central banks and governments. It's a route out of the economic traps imposed by the fiat system.
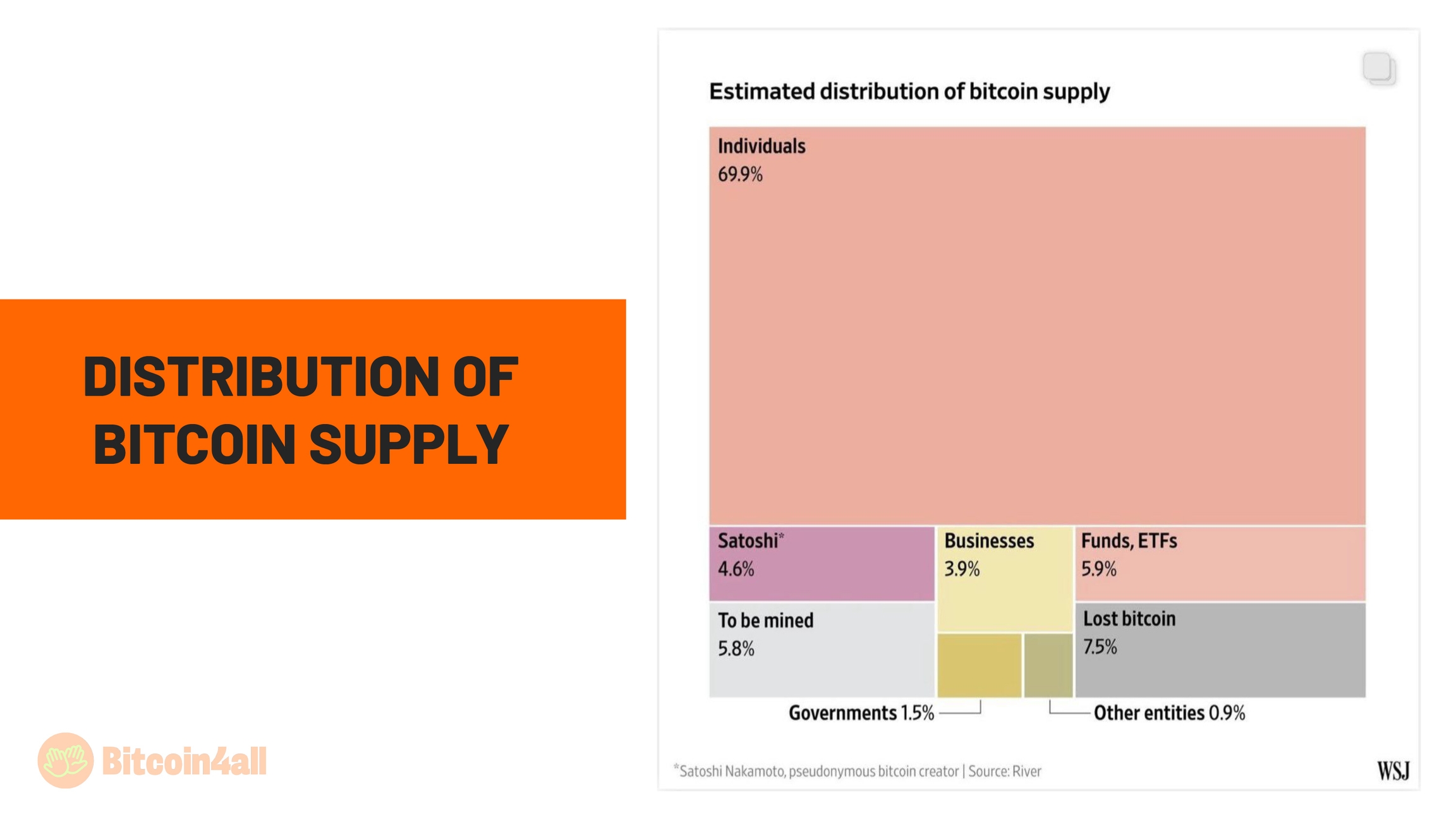
Bitcoin's distribution history reflects all this. Practically 70% of all bitcoin are in the hands of individuals, showing that most ordinary people are the main holders; 3.9% are with companies and businesses that use or invest in Bitcoin; 5.9% are in ETFs and funds, representing the entry of institutions into the ecosystem; 1.5% belong to governments, which are only now beginning to recognize Bitcoin; 7.5% are lost due to people not taking good care of their private keys; 4.6% are in addresses belonging to Satoshi Nakamoto, who has never moved or sold his balances, keeping these coins out of circulation, and 5.8% remain to be mined and will be distributed gradually until the year 2140.
Bitcoin is fairer money because the supply cannot be manipulated. It is impossible to "print" more of it. Since its inception, Bitcoin's monetary policy has been transparent and predictable, with everyone knowing exactly how and when new coins would be issued, even before the first block was mined.
The creation of Bitcoin was open and fair. Anyone can connect to the network. Unlike any other monetary system created, Bitcoin does not depend on intermediaries, does not favor elites close to power and offers a fairer alternative for individuals anywhere in the world. The rules are clear, predictable and the same for everyone. Everyone follows the same rules, without exception.

Bitcoin is incredibly powerful because it has the greatest global network effect ever seen. It is an independent global monetary network, not controlled by any country or government. No government or entity can monopolize, censor or completely ban Bitcoin, since it is decentralized and sustained by a global infrastructure of independent users, miners and nodes that verify everything.
Bitcoin's network effect is unparalleled, surpassing any monetary network of the past or present. The more people and initiatives adopt it, the stronger and more valuable the network becomes, creating an exponential growth cycle resistant to external interference. This combination of independence and network effect makes Bitcoin a money revolution. It is much more robust and resilient than any monetary system ever created. That's why Bitcoin is better money: because it's not just money, it's a superior financial system.
It unites everything in one place, a true 3 in 1. Unlike fiat money, which is fragmented, with each country having its own currency, Bitcoin is universal. In the fiat system, commercial banks control access to money and act according to their own interests, while central banks define monetary policies and distribute money through banks. With Bitcoin, all of this is integrated into a single, global network, independent of intermediaries.
So Bitcoin is better at these three functions.
Bitcoin is money that doesn't melt away in value. On the contrary: it appreciates in value, bringing more prosperity to everyone. Bitcoin has a monetary network without depending on any bank, without a manager, without requesting any personal data. Just download a wallet and you can receive Bitcoin from anywhere on the planet without any barrier whatsoever. Also, Bitcoin is even better than any central bank because it gives more predictability, transparency and guarantee of wealth and property preservation than any central bank ever has. That's why Bitcoin is not only better money, but a better and fairer global monetary system. It benefits all countries, not just the one that owns the reserve currency in force.

Bitcoin is fully independent money, an independent financial network, with an independent, immutable and borderless monetary policy.
That's why Bitcoin is seeing more and more adoption and should continue to do so, feeding back into all of its monetary properties that we've talked about here in this lesson.
In the next class, we'll understand how Bitcoin works in detail and you'll get an inside look at the protocol. We'll dive into how mining, blockchain, halvings, nodes and much more. Until then.
Additional Resources
📢 Share this lesson!
Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Telegram
📈 Your Course Progress
Class 3 de 10 (30% completo)
Last updated
