Class 10 - Sovereignty with your Bitcoin
Class 10 - How to withdraw from exchange and have sovereignty with your Bitcoin?
🎥 Class Video
👉 Click here to watch on YouTube
Full Script
Class 10 - How to withdraw from the exchange and have sovereignty with your Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a game changer. It allows anyone to take custody of their own money and move it whenever and however they want, without anyone being able to stop them. No company or government can stop you from moving your own money or take it from you if you store it with sovereignty.
Sovereignty is the word here. You are your own bank. But to actually do this, you need to know how to use tools, wallets, and how to get your Bitcoin out of the hands of intermediaries.
In the previous lesson you learned what Bitcoin wallets are and why it's important to keep your seeds safe so that you always have access to your balance. The next step is to fill this wallet with bitcoin and start accumulating for the future. So in this lesson we'll consider that you already have bitcoin and want to send it from the exchange address to your wallet address.
But before doing this in practice, let's understand what addresses are and how a transaction on the bitcoin network works.
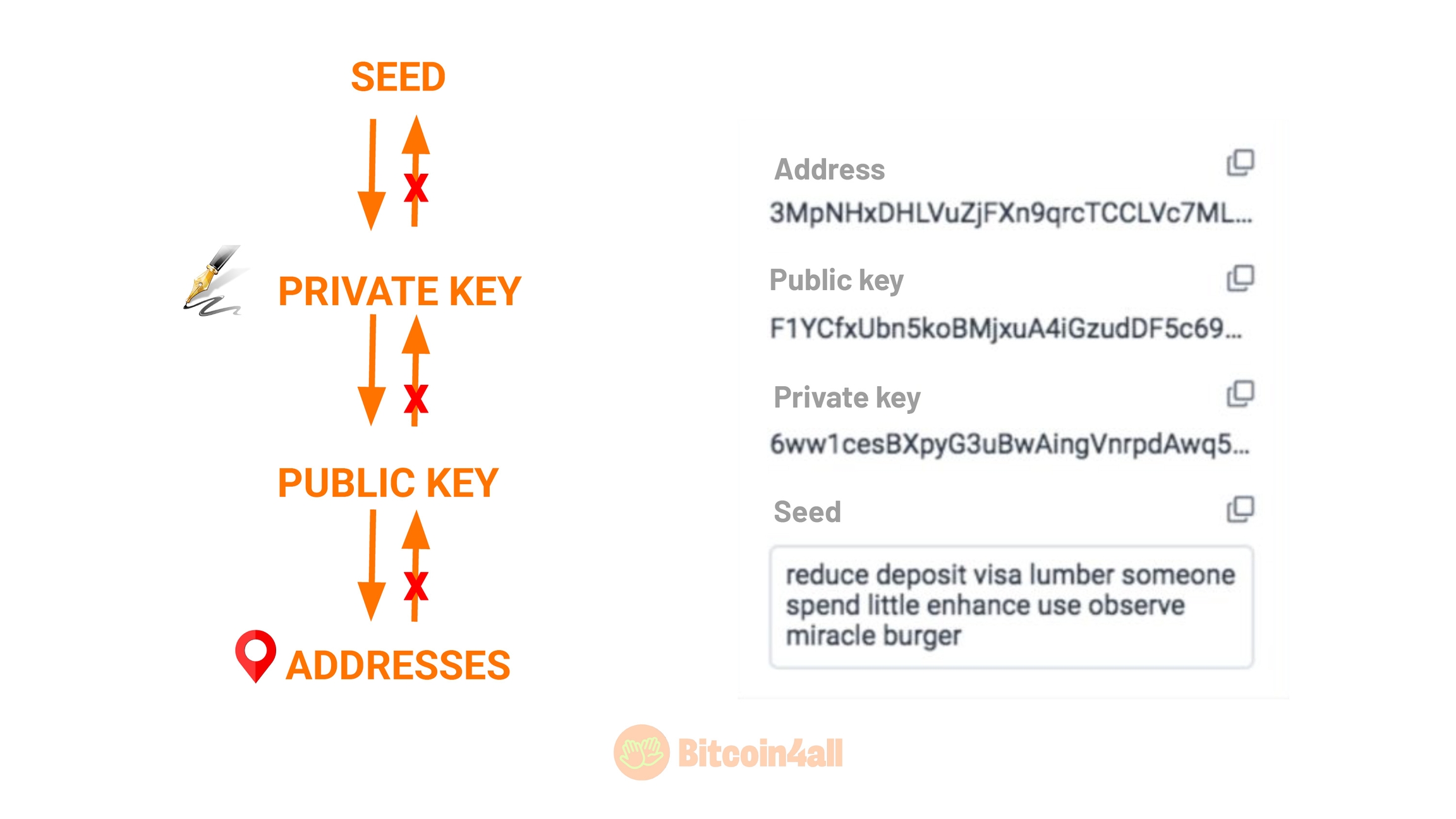
When you set up your bitcoin wallet, it generates a list of words called a "seed phrase". These words represent codes that allow you to receive, store and send bitcoin. From the seeds, your wallet will generate other encrypted codes called public and private keys.
The private key is a sequence of letters and numbers that allows you to sign transactions and control your wallet balance. With it you can move bitcoin from one address to another or import a specific balance. When you send bitcoin from one wallet to another, it is the private key that authorizes the balance to be moved. That's why you shouldn't share your seed or private wallet keys with anyone. That's why it has this name: it's private, it's information that you should keep to yourself.
The big difference between a seed and a private key is that a seed phrase (a list of 12 or 24 words) can retrieve several private keys from several linked balances, while a private key only retrieves the balances of the addresses it generated. It's in these addresses that you will receive bitcoin.
The addresses are generated from these keys and are public. When you make a transaction, they appear on the blockchain for anyone to verify your transaction. It is not possible to find out the seed or the private key from an address, even if it appears on the Bitcoin blockchain. But if you don't take good care of the seeds or private keys, then the person will have access not only to your bitcoin, but to all the keys and addresses they generate.
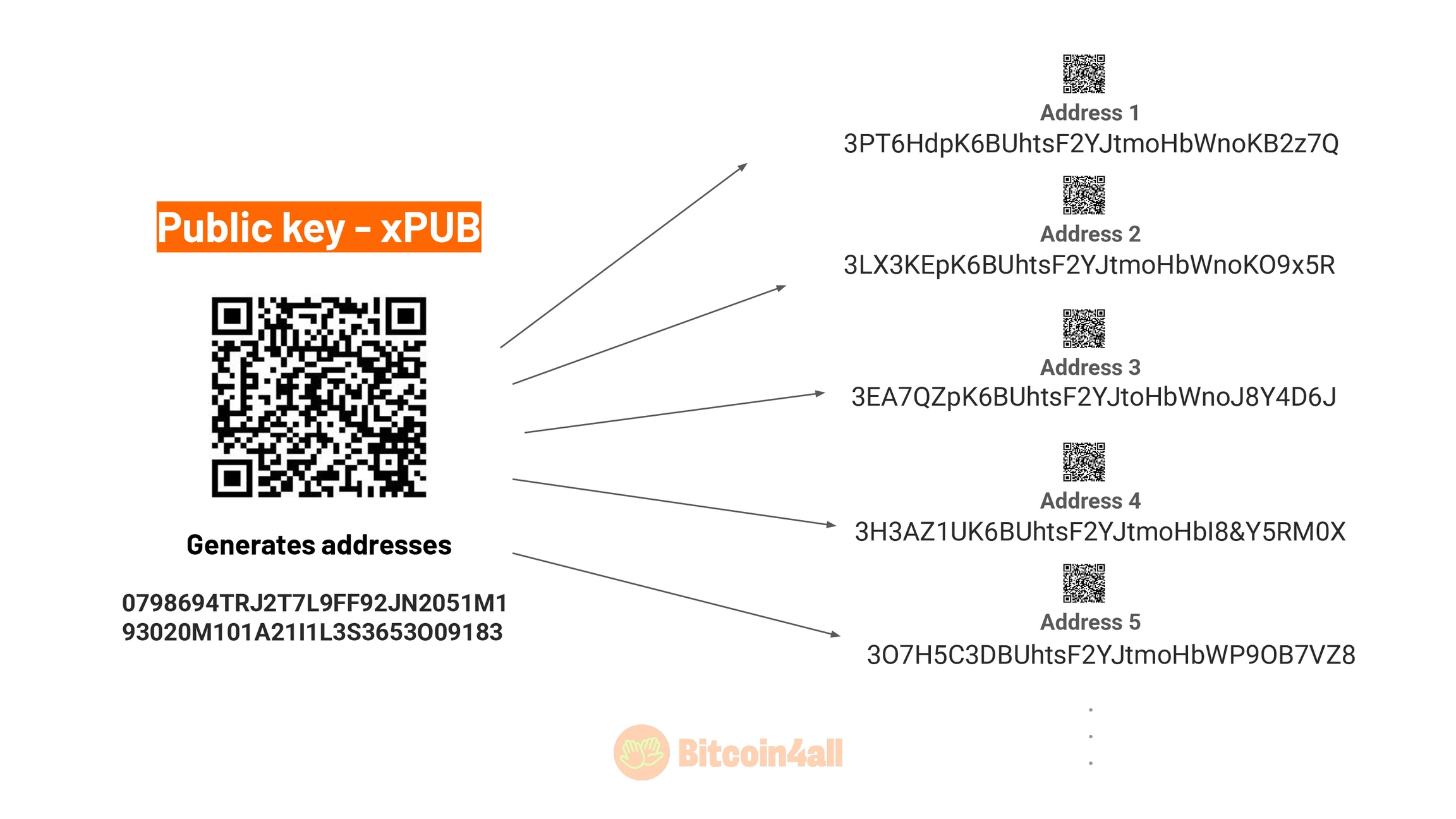
A wallet can generate thousands of different addresses from the public key. Its function is to generate addresses. One of the best practices with Bitcoin is to never reuse addresses. Wallets are always generating new addresses after you've made a transaction, precisely to give you more privacy and prevent reuse. If you've ever used a Bitcoin wallet, you'll notice that the address changes with each transaction -- this feature is there on purpose. After all, once a transaction has been made, the addresses are publicly visible on the blockchain and it would be easier to track balances by association.
In short, a private key unlocks the wallet owner's "right to spend", move and trade the coins associated with that wallet. As the name implies, it's private and you shouldn't show it to other people. The address is where you will send Bitcoin when you make a transaction. No one can guess your private key from your address.

You can think of the address as your home address. You share it with other people, it's relatively public, but you don't go around with a megaphone telling everyone where you live. Sometimes you need to show your address to receive a delivery, but that doesn't mean that anyone else will be able to access your home. For that, you need the keys to the door. In the case of wallets: the private keys.
So the address is like your home address and the private keys are what gives you access to what's inside: your bitcoin balance.
Remember that your bitcoin are not stored inside the wallets. They are always on the blockchain. Bitcoin are always in an address on the blockchain network and not inside the device itself. When you make a transfer, you tell the network that you want to move "X amount" in bitcoin from one address to another address. The wallets have the function of authorizing these transactions that take bitcoin from one address to another through a digital signature made with the private key.
But how does a transaction work?
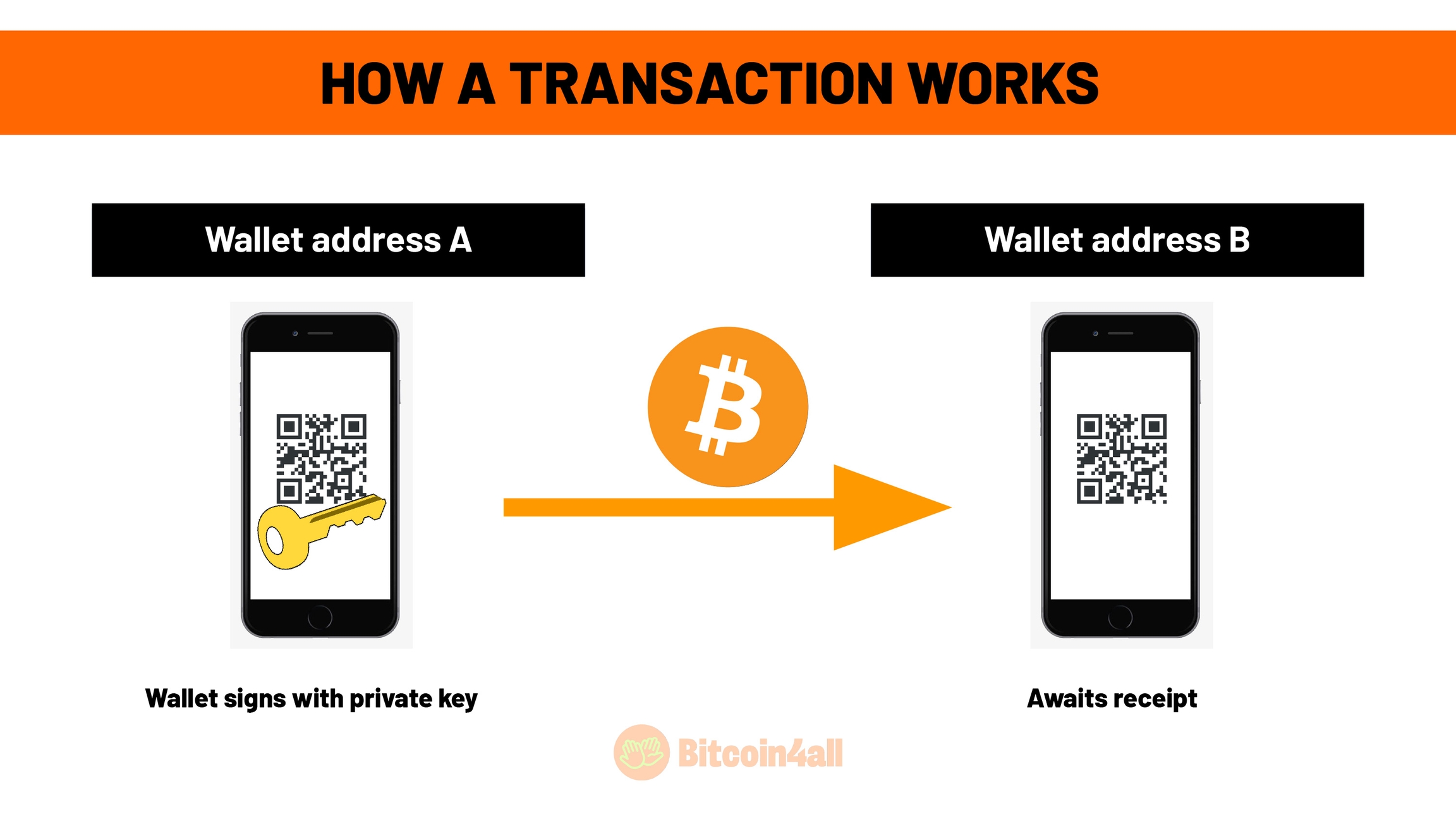
You open your wallet, type in the amount you want to send, paste in the receiver's address and click on "Send". When you click on "Send", you are signing the transaction with your private key. That's what happens behind the codes in the wallet.
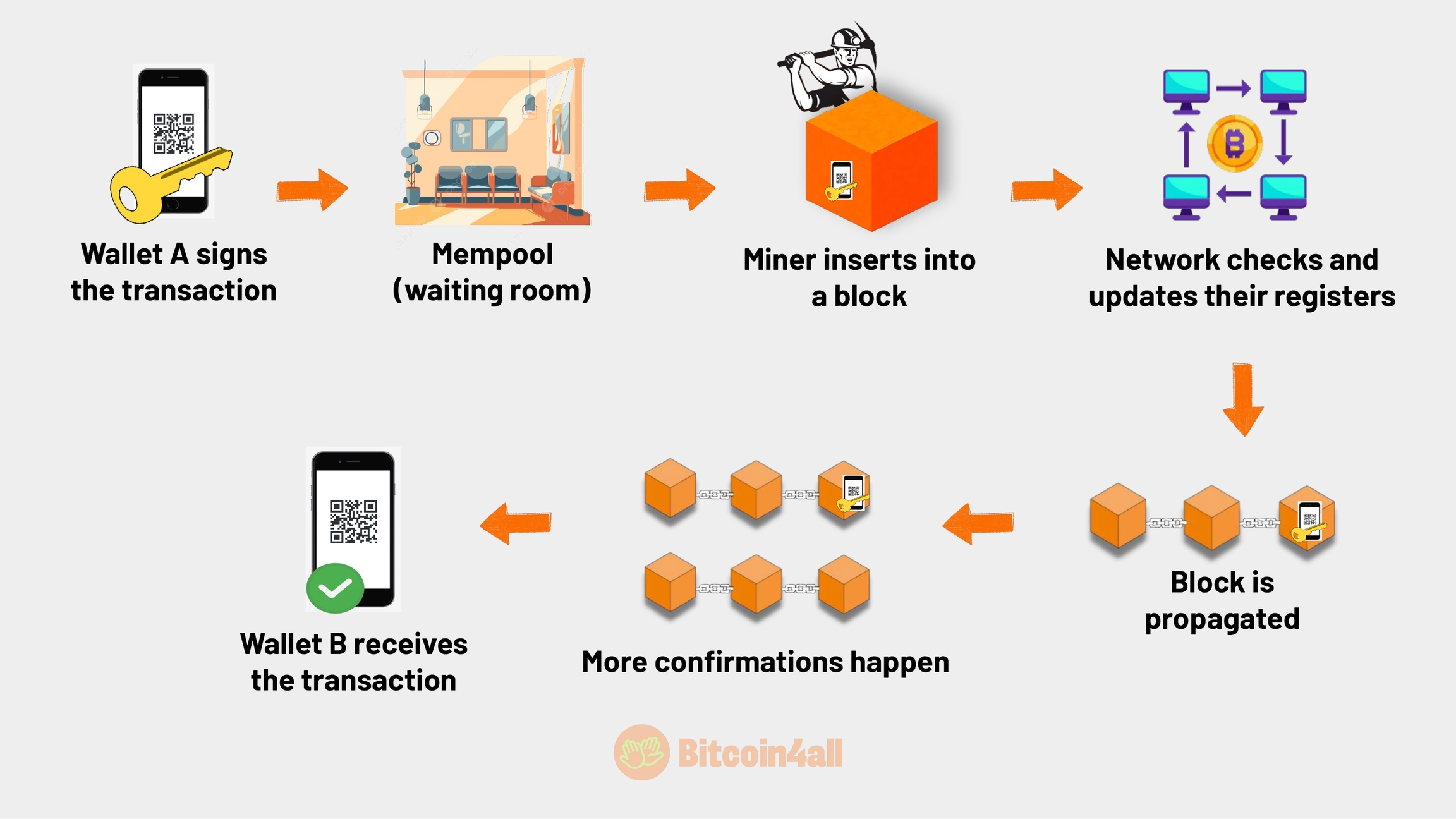
When you sign the transaction proving to the Bitcoin network that you are the true owner of the wallet address's private key, that transaction goes to a waiting room, known as a mempool. This is the waiting room for the transactions that are waiting to be inserted into a block by the miners. Transactions are recorded on the blockchain when a miner selects the transactions to be part of the block of information. As soon as a miner enters a transaction into a block, that block is verified by the network and it updates its blockchain records. This block is then propagated throughout the network as a valid block, with the transaction inside it.
When a transaction is inserted into a block, it is said to have been confirmed. As more blocks get mined, more confirmations occur. Generally, a transaction is considered irreversible after 6 confirmations, when six blocks have passed. When the confirmations take place, the wallet notifies the user, the transaction is considered to have been received and the balance is available to be spent. This is how on-chain transactions happen when you send bitcoin.
Now that you've understood the theory, let's get practical!
Let's show you how to set up a wallet from scratch, withdraw bitcoin from the exchange to this wallet and recover the balance using the seed phrase.
For this tutorial we chose to use the Sparrow Wallet. It is a very versatile and complete wallet for both beginners and advanced users. It is self-custodial, open source and works very well as a coordinating wallet between various hardware wallet brands: Jade, Ledger, Trezor, Coldcard, Seed Signer, Krux... That is, practically all hardware wallets work with Sparrow. The difference is that wallets that have their own software, such as Ledger and Trezor, require you to download their software, Ledger Live or Trezor Suite, in order to update the device's firmware before connecting to Sparrow.
It also offers features such as creating multisigs, making air gapped transactions, PSBTs, managing and consolidating UTXOs, possibilities that focus on increasing wallet security and privacy. Remember that Sparrow is a desktop wallet only. It doesn't have a mobile app for iOS or Android. We'll leave the link here Sparrow Wallet on the screen for you to download, alongside with a list of other wallets for you to try out and see which one suits you best. 
Let's start by configuring Sparrow. The first step is to download Sparrow and install the software.
(video) Then just open Sparrow and click on "New wallet" to create a new wallet. 
(video) Now just choose a personalized name for this wallet, I'll type "btc4all tutorial" and click on "Create wallet". 
(video) This is Sparrow's homepage. Notice how the left column is gray and only the settings are blue. This means that it is totally blank and you need to create a wallet, import one or connect one so that you can keep track of balances, receive and send Bitcoin.
The "Settings" section shows the type of configuration: "single sig". This configuration means that you only need one key to sign transactions from this wallet and only one list of words to retrieve the balance. Below is the type of script and a few more technical details. 
Notice how four boxes appear in the "Keystore" field with different options. These are all different ways of using Sparrow. You can connect your hardware wallet device to Sparrow and move your balances through it. You can create an air gapped wallet where you never have to plug the device into your computer to sign transactions. You can create from scratch or import a wallet you already have and use Sparrow as a hot wallet or you can create a watch only wallet to just keep track of the balance and not move anything.
Let's click on "New or imported software wallet" to create a wallet from scratch and show you how key creation works. 
(video) Here are a few ways to create wallet recovery words. First, let's click on the first option, "Mnemonic Words", and "Use 24 words". 
(video) The list of empty words appears here. After clicking on "Generate new", the wallet will generate the words.
(video) Done. Now let's just write them down carefully in the order in which they appear. After doing that and clicking on "Confirm backup" we'll confirm that we've written everything down.
(video) Sparrow will ask to type in the words to confirm that we've really written everything down. Note that until the process is finished, the "Checksum" icon appears as invalid.
(video)
When the last word of the seed phrase is entered, the checksum changes to valid, signaling that a sequence of words valid for a Bitcoin wallet has been entered. The next step is to click on "Create Keystore" in the blue box.
(video)
Then click on "Import Keystore".
(video)
That's it. The seed data and all the keys generated have been imported. Now let's just click on "Apply" in the bottom right-hand corner of the screen. The wallet will ask if we want to create a password to protect the wallet in case someone gains access to the computer being used. For this example, we're going to click "No password", but you should have a password to add another layer of security to your wallet.
(video)
Now notice how the left column has suddenly turned blue. This means that the wallet is now ready to receive bitcoin, send and manage addresses.
Well, now let's show you how to send bitcoin to this wallet and recover the wallet to test that everything is OK before sending larger amounts. It's important to do this so that you can check that everything is working properly before sending all your hodl stack to this wallet.
Let's click on "receive".
(video) Now, I'm going to copy the code that appears in the "address" field. This is my address on the Bitcoin network. I'll show you how to send bitcoin here to this newly created wallet. To do so, I'll withdrawing Bitcoin from an exchange. I'll only use Coinbase as an example. The procedure is the same on other platforms.
(video) Well, here I have 43 dollars in Bitcoin, so I'm going to withdraw that amount from the exchange.
To do this, I'll click on the grid in the left corner of the screen.
(video) Now I'll click on "Send".
(video) I'm going to paste Sparrow's Bitcoin address, which I've already copied, into this field at the top of the page.
I'm going to select "Bitcoin".
(video)
Afterwards, I'll select the Bitcoin network. All other networks are not Bitcoin, so be careful not to mix them up.
(video) Now I'm going to enter the amount I want to withdraw and click on "Preview" to see if the information is correct.
(video) Everything's fine here.
I'll click on "Send now".
(video) That's it. Withdrawal confirmed.
Now all you have to do is follow up with Sparrow when the transaction is confirmed. It should take a few minutes for the network to process this transaction.
(video) Done, the transaction arrived here at Sparrow: 40,633 satoshis are now in my custody.
Now let's imagine that I've lost access to this balance in my wallet and I'm trying to recover it from scratch. Then we'll see if the balance will reappear.
(video) I closed the wallet I created earlier. Now, let's click on the third option, "Import wallet".
(video) Several ways to recover will be displayed. I'll go with the first one, which is the way I generated it before: with 24 words.
(video) Now let's just enter the same words I wrote down when I created the previous wallet and click on "Discover wallet".
(video) It will ask me to create a name for the wallet I want to import. I'll type in "Backup recovery" and click on "Create wallet".
(video) Done. Sparrow retrieved all the data, the keys and my bitcoin balance.
Now I'm going to do the same recovery process on a different Sparrow wallet so you can see how, regardless of the application or software you use, it is possible to recover your bitcoin balance if you have your backup word list. So I'm going to backup that same wallet on Blue Wallet, a well-known mobile wallet that's very easy to use.
(video) I'll open my Blue Wallet on my cell phone and click on "Add Now" to create a new wallet.
(video) I'll select the last option, "Import wallet".
If you want to create a wallet from scratch, just select Bitcoin and then click on "Create". But right now I want to recover the wallet I created in Sparrow, so I'll go straight to the import option.
(video) I'm going to type in the 24 words I generated in Sparrow in order and make sure I type them correctly. I'll click on "Import" when I'm done.
(video) There we go. Blue Wallet has found the wallet.
I'll click on "Import".
(video) Clicking on it shows the balance I transferred from Coinbase.
That's one of the wonderful things about Bitcoin: since it's open source, you can recover your balance on any device that follows the same initial rules you used when generating your keys.
Now that you've been through all the Bitcoin4All lessons, you're ready to start accumulating and exploring the world of Bitcoin.
I hope you enjoyed Bitcoin4All and that this was just the beginning of your learning journey. After all, Bitcoin isn't just a technology, it's a universe of concepts that unites economics, cryptography, decentralized networks and continuous innovation. Every single day, new developments and ideas emerge, challenging our traditional notions of money and sovereignty.
Share this course with friends, relatives and other people who are also curious and want to learn about Bitcoin.
Until next time and Opt Out!
Additional Resources
📢 Share this lesson!
Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Telegram
📈 Your Course Progress
Class 10 de 10 (100% completo)
Last updated
