Class 1 - What is Bitcoin and why was it created?
🎥 Class Video
👉 Click here to watch on YouTube
Full Script
Class 1 - What is Bitcoin and why was it created?
More than 15 years ago, Bitcoin was born as a revolutionary idea, and since then, it has gone from something unknown to becoming one of the most talked about topics in the world. Today, many people have heard of Bitcoin or have an opinion about it. But, unfortunately, for many, it is still seen as just something for nerds, a risky investment or something that is only good for financial speculation. This limited vision ends up ignoring the true purpose and enormous potential of Bitcoin: to be accessible money for everyone.
And what not everyone realizes is that Bitcoin wasn't created just for investors, tech nerds or big companies. It was designed to be a fairer and more transparent financial system. Money that anyone, anywhere in the world, can use. Bitcoin is a powerful tool for protecting wealth and ensuring financial freedom.
Today, more than ever, it is important to understand how Bitcoin can make a difference in your life. With inflation rising, money losing value and people trusting banks and governments less and less, Bitcoin presents itself as a reliable alternative: money that is truly yours, that no one can block, confiscate or devalue for no reason. With Bitcoin you can become your own bank and no longer depend on intermediaries to store or control your money.
Bitcoin is not just a currency and a technology, it is also an invitation for us to rethink our relationship with money and how we can build a new financial system that is freer, safer and more accessible for everyone.

When most people think of money, they immediately imagine paper bills or the balance in their bank account. In other words, the idea of money that most people understand as true is directly linked to something controlled by third parties, such as banks, brokers or values ÔÇïÔÇïcreated by governments through central banks in paper notes.
Bitcoin is different. It is digital money that does not depend on governments or banks, and you do not need to trust these institutions that, throughout history, have failed many times. Although the idea of digital money may seem new, it is actually the result of centuries of research, trial, error and learning.
Throughout history, many brilliant minds --- physicists, Austrian economists, computer engineers and investors unhappy with inflation have imagined that something like Bitcoin would one day exist.
Tesla and Henry Ford envisioned the creation of energy-backed money that would promote peace. Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman, Austrian economists, pointed to the problems of leaving monetary policies in the hands of governments and how digital money, moved through the internet, could bring more prosperity to people by being resistant to corruption and unstoppable.
So realize that Bitcoin, in a way, has always been there as an idea waiting for the right time to become reality. But what these geniuses of the past didn't know was how exactly this digital money would be created or what technological advances would make it possible.
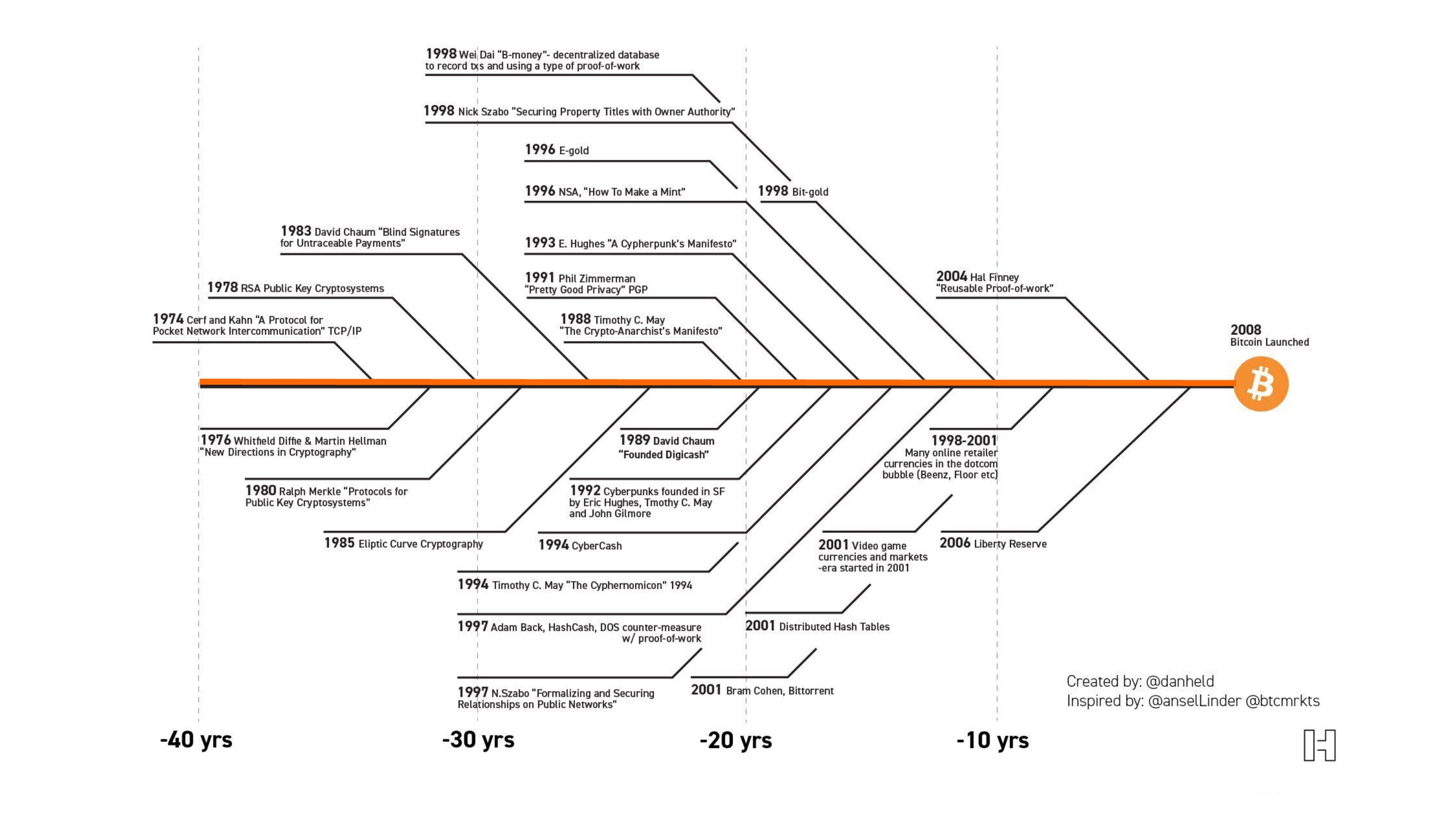
Those who took the first steps towards Bitcoin were the cypherpunks of the past. Since the 70s, these cryptographers have been trying to create money that can be used on the internet. But none of the projects worked as expected. And that's why it is said that Bitcoin did not appear overnight, it is a discovery that was ready to happen. Bitcoin is the result of 40 years of previous research and attempts. Several projects over time paved the way for the creation of Bitcoin, each contributing a piece of the puzzle that Satoshi Nakamoto finally put together in 2008.
That's why many people say that Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin, didn't invent anything, but rather discovered Bitcoin. This is because he learned from the failures and successes of these previous projects and this knowledge was crucial for Satoshi to be able to create something that really worked.
Ok, but then how did Bitcoin come about?

The first records of Bitcoin begin with an email on October 31, 2008. On that day, an anonymous cypherpunk named Satoshi Nakamoto posted on a cryptography mailing list that he was working on a paper about an peer-to-peer (P2P) electronic cash system, without the need for trusted intermediaries.
!(slide 4)[https://github.com/areabitcoin/Bitcoin-4-All/blob/main/Bitcoin%204%20All%20-%20English/Slides/Class%201/slide-04.jpg]
In this email there was a link to the Bitcoin Whitepaper, a document with just 9 pages that technically describes the functioning of the Bitcoin network. The text explains how digital signatures send and receive transactions, how these transactions are grouped into blocks and how proof of work, through the use of computational power, solves the problem of double spending and, at the same time, generates new coins as a reward for network participants, in the process known as "mining".
Double spending was one of the biggest challenges in creating digital money and many cypherpunk projects of the past failed precisely because they were unable to solve this problem without centralizing control of the network. But what is double spending? Double spending is when you can spend the same coin twice. To give an example, it would be like paying the bill at the bakery with a 50 dollar bill and then it reappears in your wallet so you can spend it again. This would make the system useless as money.
The word Bitcoin appears only twice in the whitepaper: in the title and in the link to the website. The word "network" is mentioned 21 times. This shows how Satoshi was focused on the architecture of this P2P network and how it would work in a decentralized way, without depending on intermediaries with decision-making power over the protocol.
Satoshi also made available the whitepaper on the website bitcoin.org, where he continues available to this day, translated into Portuguese and more than 40 languages. An interesting fact is that the bitcoin.org domain was registered on August 18, 2008, a few months before the publication of the whitepaper, which shows how Satoshi was already preparing the ground to present this creation to the world.
It's usually possible to find out who registered and owns a domain, but Satoshi thought of everything and kept this information anonymous. Satoshi Nakamoto's decision to remain anonymous is one of the most intriguing aspects of Bitcoin's emergence. The exact reasons behind this choice are unknown, but several theories have been floated. To this day, no one knows who Satoshi is, whether he is a person or a group of people, and in the end it doesn't matter. The fact that Bitcoin doesn't have a known creator is actually a positive thing, because it reduces any noise between Satoshi's personal life and Bitcoin. Satoshi's anonymity helped Bitcoin grow as a truly global, decentralized and organic system, without the need to depend on or be tied to a central figure.
Satoshi Nakamoto stayed for a few more years working on the code and exchanging ideas with other cryptographers around Bitcoin. Then, in April 2014, he handed over control of the website bitcoin.org, and bitcoin repository, to developer Gavin Andresen. Satoshi stood on the shoulders of giants by merging past cypherpunk projects and going further by making Bitcoin a reality.
Bitcoin is the result of the combination of several technologies. Separately, these technologies would not have the same characteristics and properties that make Bitcoin unique. It is this union that made it possible to create something so revolutionary.
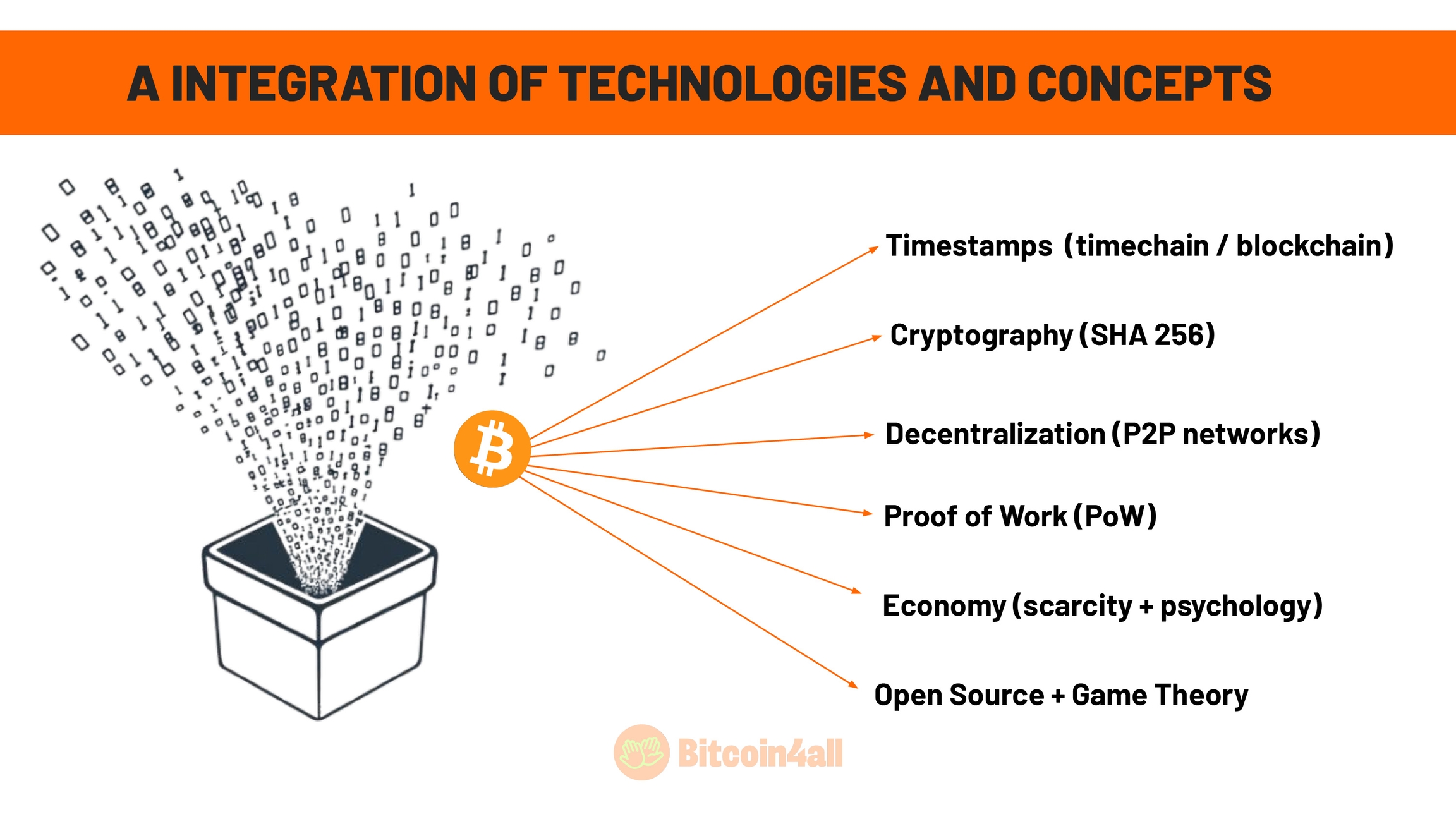
The first technology Satoshi used was timestamps, date and time registers that create a timeline (a timechain) that cannot be modified.  This timeline is essential to ensure that records cannot be altered. Many people know this timeline as "blockchain", where blocks of information are connected to each other. These blocks record transactions immutably and in the order in which they occur, ensuring the integrity and transparency of the system.
Satoshi also used encryption and cryptographic algorithms, such as SHA-256, to make the network work securely through codes and algorithms. This means that only those who have the correct "key", that is, only those who know the answer, can move funds. Cryptography is a fundamental technology in the Bitcoin network as a whole.
Furthermore, Satoshi incorporated P2P (peer to peer) network concepts, where anyone can run a node and connect to the network without needing to ask anyone for permission and it is this principle that underlies decentralization and network architecture. The nodes connect to each other to form a distributed network for verifying and storing transaction records, without depending on institutions or intermediaries. This architecture is what guarantees the independence and resilience of the system.
Satoshi also used proof of work, which guarantees that it is not possible to create money out of thin air. You have to prove to the network that you solved a problem, followed the consensus mechanism and that you deserve to receive coins as a reward for having provided a service to the network using your computational power. There is no way to falsify proof of work, and that is what brings trust to Bitcoin. It ensures that the rules for creating each block of information were followed in accordance with the consensus that the entire network follows. This mechanism is the basis of Bitcoin's integrity and immutability.
Satoshi established a maximum limit of coins that can be created: 21 million units. This limit is reached through a mechanism called halving, in which every 4 years on average the issuance of new coins drops by half until the last bitcoin is created. This maximum limit is what gives Bitcoin unique monetary properties, in addition to its digital characteristics. It reflects fundamental economic concepts such as scarcity, ensuring that Bitcoin cannot be arbitrarily inflated, as is the case with government-issued currencies. This characteristic makes Bitcoin a sound and predictable store of value.
Finally, Satoshi also kept the entire Bitcoin project open source, that is, accessible and public. This means that anyone can check it, collaborate on its development and even copy the code. This decision made Bitcoin radically transparent, something no central bank or traditional monetary system offers. Transparency is what allows public verification and free access for anyone anywhere in the universe. Bitcoin is the most accessible, inclusive and open network ever created, offering equal opportunities for everyone who wants to participate.
Before Satoshi, no one had mixed all these technologies into a single protocol. In class 4, on how Bitcoin works, you will better understand each of these points.
Two months after sending the email to the Cypherpunk mailing list, launching the website, and making the Whitepaper available for anyone to verify, collaborate on, or even copy, Satoshi mined the first Bitcoin block.
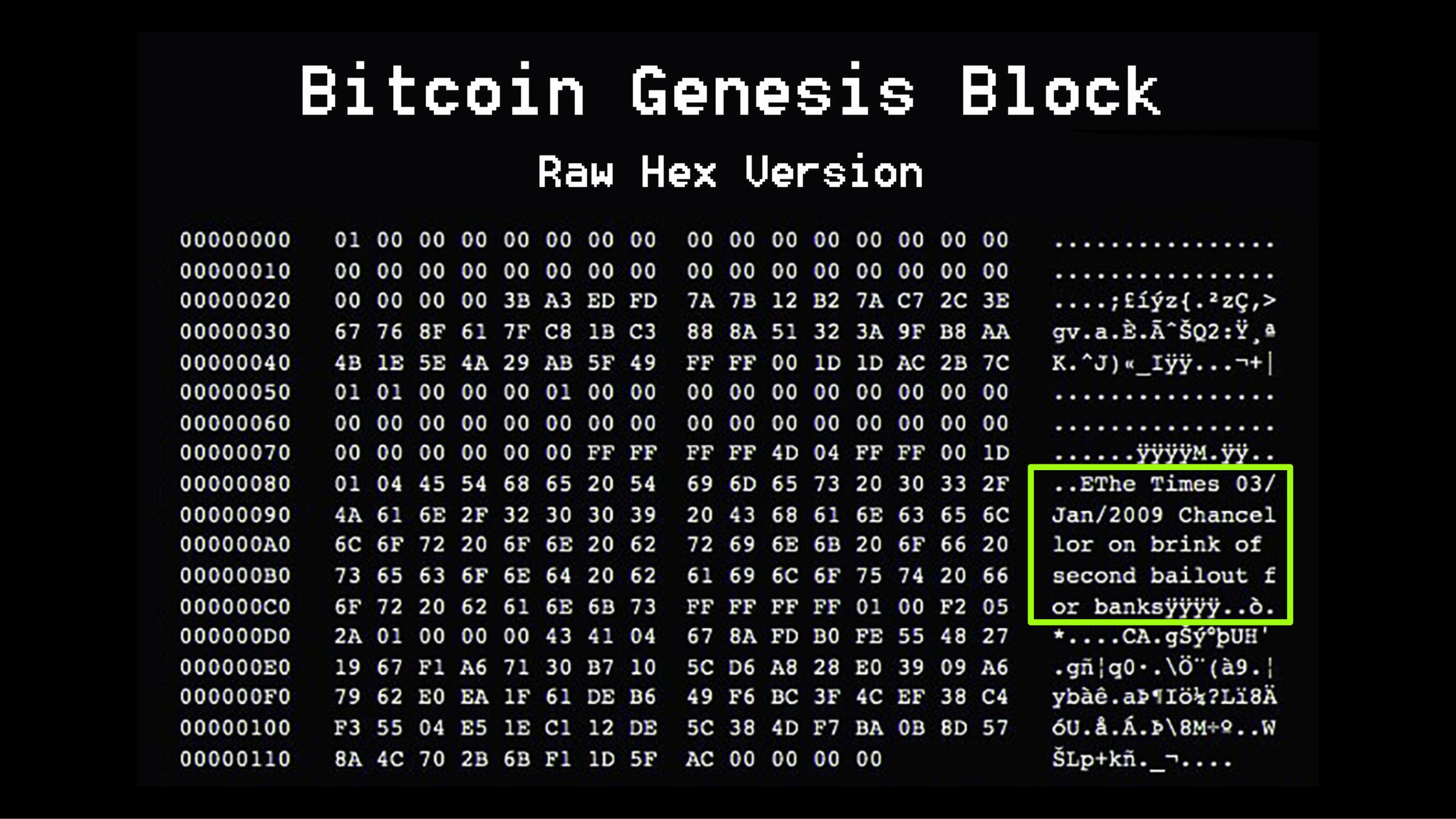
This first block mined on January 3, 2009 is called the "genesis block". Satoshi received 50 Bitcoin as a reward and the most curious thing is that this block contains a message, a quote, left by Satoshi himself:
"The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks" - this is the title on the cover of the British newspaper The Times from January 3, 2009. This cover here:

It shows how the history of bitcoin is directly linked to recent major global crises. Bitcoin emerged precisely when the 2008 crisis broke out, as a response to the manipulation of the economy and centralization carried out by central and commercial banks. The quote from The Times was not for nothing: it reinforces the criticism of the traditional financial system.
This report pointed out that in 2009 the British chancellor would rescue a bankrupt bank for the second time. This gives us several clues about the reasons that led Satoshi to create Bitcoin and what he thought about the financial system.
In messages written on internet forums, Satoshi demonstrated how in-depth he had knowledge about how the economy works and how he saw Bitcoin as a completely opposite alternative to the traditional system. He created a decentralized currency, which cannot be confiscated, monopolized or devalued by any government or bank.

For all this, the way Satoshi launched Bitcoin to the world was completely fair.
All Bitcoin were created following network consensus, without pre-mining. Pre-mining is when project creators issue a number of coins to themselves before the network starts running. This ends up creating a disproportionate privilege for founders. Furthermore, the whitepaper was published before the first block was mined, in a completely transparent, public and open source way, giving more people the chance to collaborate or even copy the code before the Bitcoin network even started operating.
Bitcoin operated for almost a year and a half without having any monetary value, it literally worth ZERO. This allowed Bitcoin to circulate freely and the network to decentralize organically.
The growth of the Bitcoin network was completely organic because there was no initial investors, no venture capital participation and no expectation of profit. It was a protocol maintained by cypherpunks who were discovering how that whole stack of codes could work and evolve.
And unlike all the other founders of digital currency projects that emerged later, there are no records of Satoshi having sold even one Bitcoin.  He created Bitcoin and, after building the basis of the protocol, disappeared without ever making a profit. Satoshi left Bitcoin as an invaluable legacy to humanity, without taking anything in return.
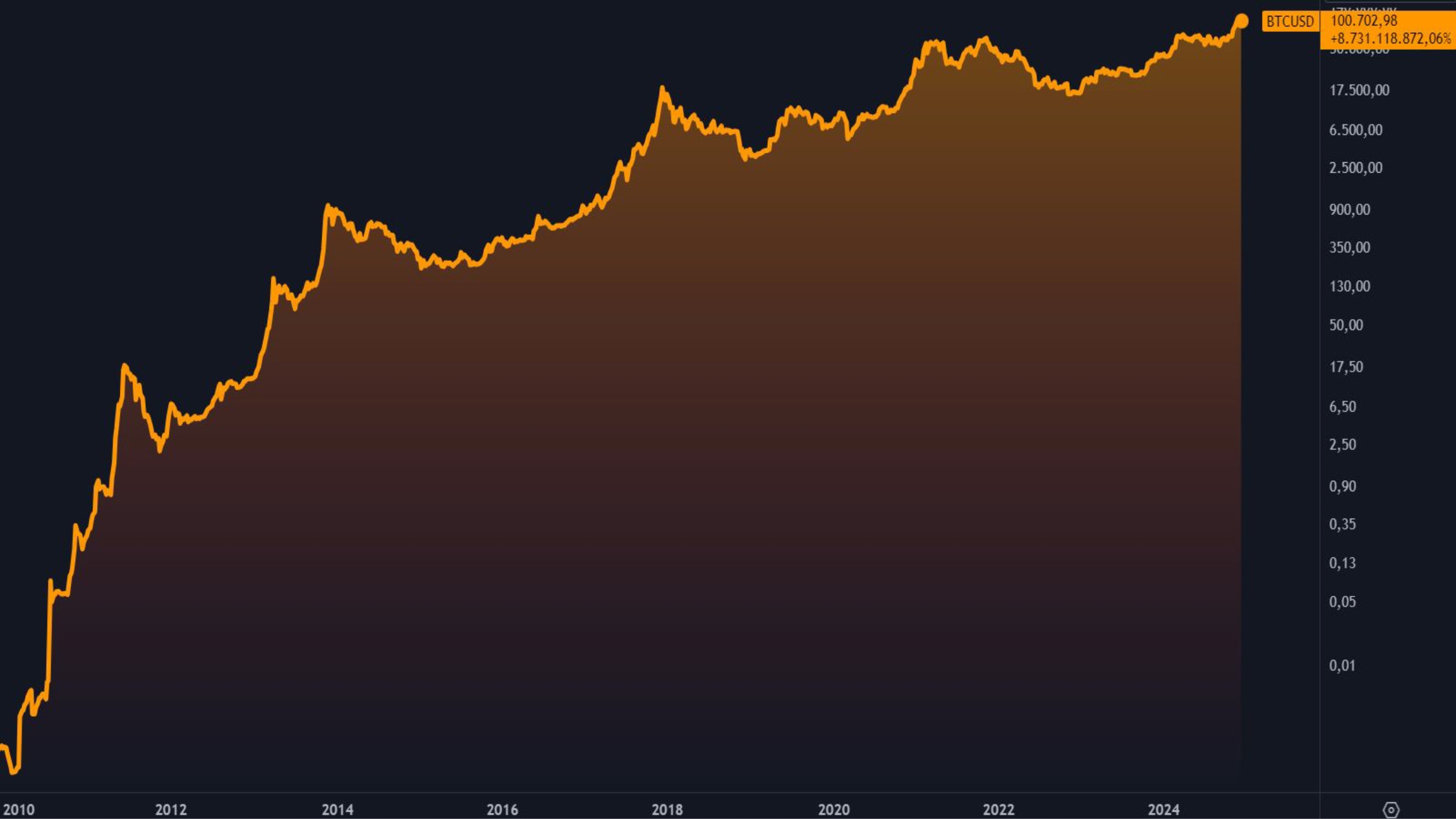
Since then, Bitcoin, which was initially worth nothing, has reached new highs with each appreciation cycle. It reached $100,000 at the time I am recording this class and has appreciated more than 7 billion percent in dollars since 2010, when it began to be traded and priced by the first online platforms.
The price of Bitcoin attracts attention, arouses curiosity, enchantment and greed, but in fact it is a reflection of the growth in adoption of a new financial system. For the first time in human history, we are witnessing and documenting the birth of completely digital money, independent of governments and banks. The great appreciation of Bitcoin reflects its growing demand and with this the price can also tell a story. It shows the ups and downs of Bitcoin, but most of all, it symbolizes the impact of this revolutionary technology over time.

The history of Bitcoin is full of important events. In just 15 years, a lot has already happened, and these past events help us understand how we can better deal with what lies ahead.
Well, you already know the first two milestones: in 2008 the whitepaper was released and in 2009 the bitcoin network started running.
In 2010 the first transaction took place with Bitcoin, which even became a date commemorative: Bitcoin Pizza Day. On the day May 22, 2010, Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10 thousand bitcoin for two pizzas, which at the time were worth about $25. Today, those pizzas would be worth billions of dollars, but Laszlo's gesture was much more than a simple payment. It reinforces the importance of Bitcoin as money that can be used on a daily basis and reinforces its essence as a P2P tool.
Although it seems like Laszlo's mistake and a waste when we look back, Pizza Day highlights the importance of adopting and circulating Bitcoin as money. Laszlo showed that Bitcoin can be used in a practical way, without depending on banks, exchanges or intermediaries. To have Bitcoin, you just need to find someone willing to exchange a product or service for Bitcoin. It is the most sovereign and independent form of negotiation between two people.

Another important milestone in the history of Bitcoin happened in October 2013, when the Silk Road platform was closed. Silk Road was an online marketplace on the Deep Web that allowed the trade of products and services of the most diverse nature through Tor and Bitcoin.
Created by Ross Ulbricht, Silk Road aimed to be a truly free market where users could anonymously trade anything, relying on the principles of consent and privacy. It was a bold experiment in an unrestricted market, where people were free to exchange goods and services without interference from governments or corporations.
Silk Road offered hundreds of products, equipment, services and even drugs.  All products and those who worked on the platform were paid 100% in Bitcoin. At the time, bitcoin was worth around 50 cents. The goal was to be like Amazon or Ebay, but completely free and backed by Bitcoin.
However, the success of the platform caught the attention of authorities. Silk Road was eventually shut down, and its founder, Ross Ulbricht, was arrested and sentenced to life in prison. This is because, although Ross had good intentions,, Silk Road quickly became a marketplace for trading drugs and illegal products, even though the platform had internal rules prohibiting the sale of these items.
During the operation, the American government seized more than 200 thousand bitcoin from Silk Road, and thus became, ironically, one of the largest holders of Bitcoin in the world. Ross' sentence is seen as disproportionate, unfair and politically motivated, especially as lighter sentences have been imposed in similar cases.
Ross's case also raised a global debate about a website owner's responsibility for behavior of its users. Although Ross's family managed to raise 1 million dollars to pay his bail, American judges did not approve his release anyway.
In 2025, with a greater understanding of the issue, social pressure for justice and political interest in Bitcoin, current US President Donald Trump pardoned Ross and released Ross from Silk Road's life sentence.
!(slide 10 - again)[https://github.com/areabitcoin/Bitcoin-4-All/blob/main/Bitcoin%204%20All%20-%20English/Slides/Class%201/slide-10.jpg] Another major milestone in the history of Bitcoin was the release of the Lightning Network whitepaper, a second-layer solution for fast and cheap payments. The lightning network began running in 2017, following the Segwit upgrade, allowing Bitcoin to be used as an everyday currency, reducing transaction costs and increasing speed, without sacrificing security and decentralization of the mainnet.
In 2017, the SegWit (Segregated Witness) update was one of the most significant changes to the Bitcoin protocol. This improvement brought greater scalability, security and flexibility to the network. SegWit reduced the burden of transactions, which lowered fees and paved the way for the development of the Lightning Network. The activation of SegWit was the result of years of debate and despite being a significant change, it did not alter the fundamental properties of Bitcoin, as it was implemented as a soft fork, ensuring compatibility with the protocol's previous rules.
Another important milestone came in 2020, when MicroStrategy became the first public company to adopt Bitcoin as part of its cash strategy. This decision attracted the attention of investors of all profiles, consolidating Bitcoin as a store of value in the corporate market and boosting its recognition in the corporate world.
In 2021, Bitcoin underwent the activation of Taproot, which also facilitates transactions, scalability and reduces data usage. That same year, El Salvador became the first country in the world to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender, showing that it is possible to migrate to the Bitcoin standard at a nation state level and inspiring other countries to consider this path.
As early as 2023, the NOSTR protocol began to gain traction. Inspired by the principles of Bitcoin, NOSTR is aimed at social networks and online content, allowing people to regain control over their own data, without depending on large technology companies, known as Big Techs.
In 2024, two major events marked the history of Bitcoin. The first was the launch of the first Bitcoin ETF in the US, which broke trading and growth records, further consolidating Bitcoin as a mainstream financial asset. The second was a historic statement by then-former US President Donald Trump, who promised to create a strategic Bitcoin reserve, highlighting Bitcoin's global recognition as an economic and strategic tool.
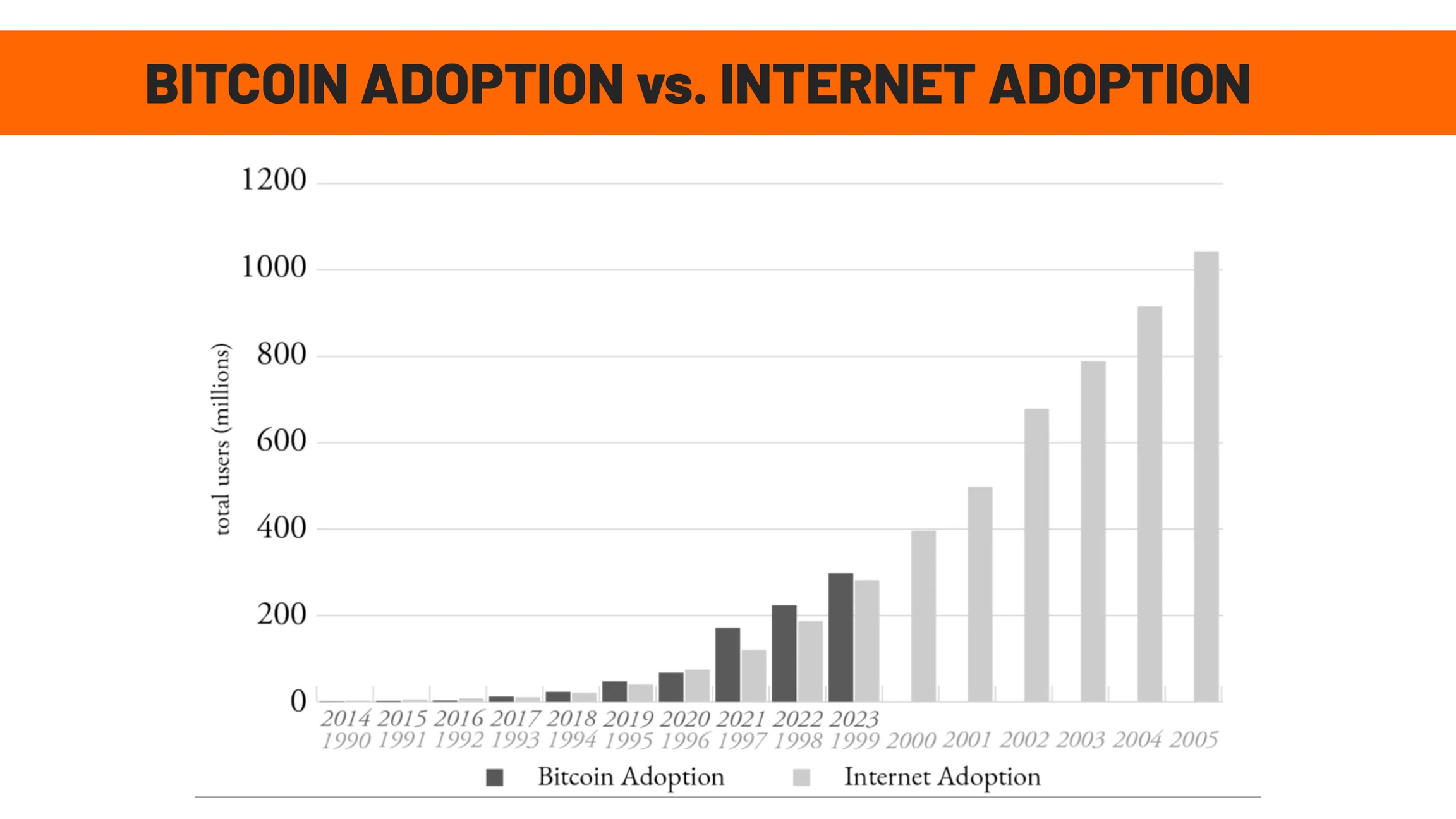
In just 16 years, Bitcoin has grown much faster than any company, commodity or country. At the same time as it rescues ancient monetary properties, it has registered exponential adoption, faster than even the internet itself. This is what appears in this image: the dark gray bars show the growth of Bitcoin, while the light gray bars represent the adoption of the internet since the 1990s. Today, Bitcoin already has the same number of users as the internet had in 1999.
And if the internet has become the main tool for accessing information, Bitcoin can become the main tool for accessing value, without depending on governments or banks. Even though it is growing faster than the internet, Bitcoin is still in the early stages of its adoption.
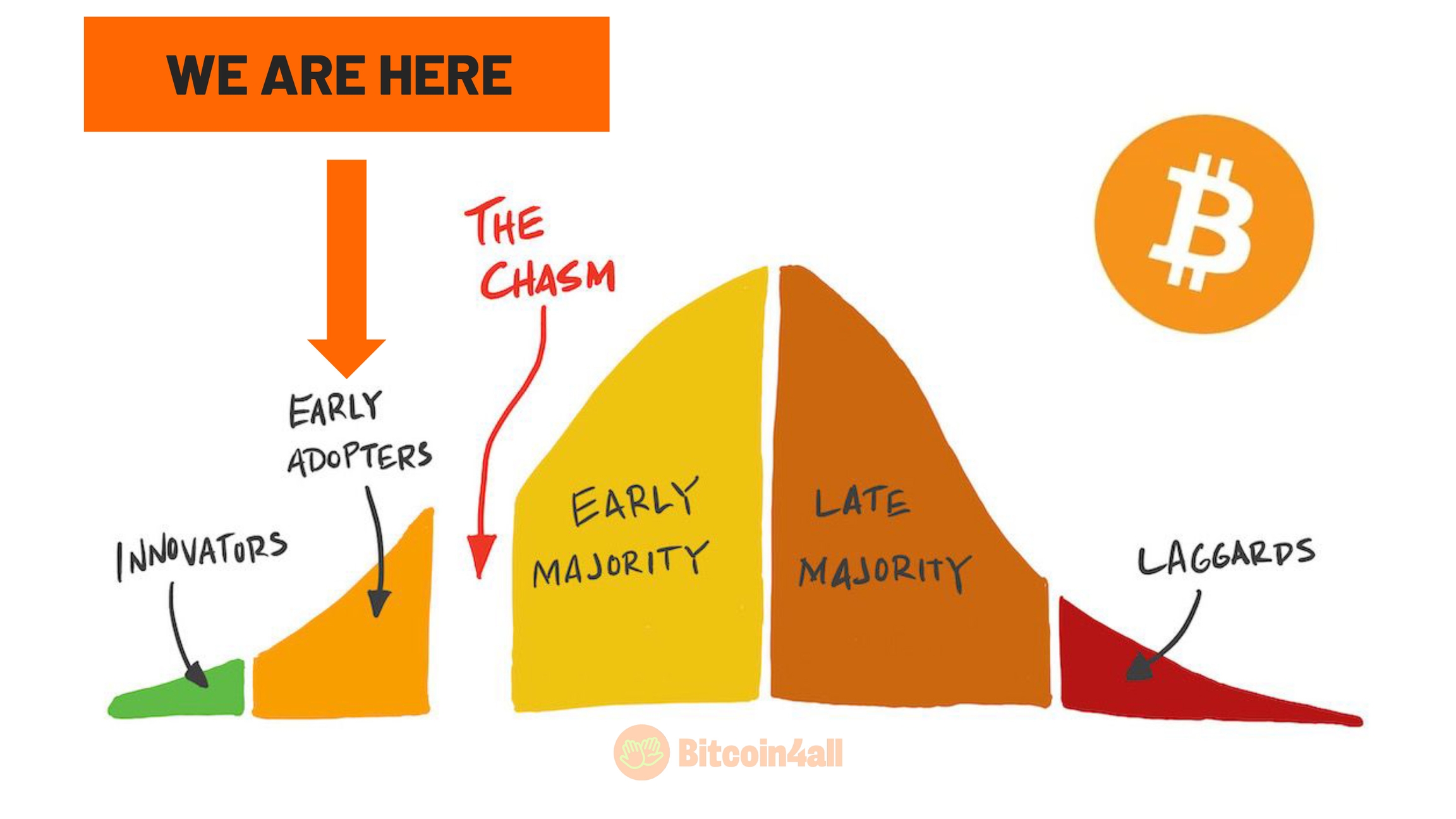
The Adoption Chasm Chart is a classic model used to explain how new technologies are adopted by people over time. It divides users into five groups: innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards. 
The most challenging point in this model is the "abyss" (or chasm), which appears among the early adopters and the early majority. This chasm represents the critical moment in which an innovation needs to stop being something niche and become a technology that is widely accepted and used in everyday life. Many technologies do not even reach this point of the chasm.
In the case of Bitcoin, the chasm represents the transition between those who adopt Bitcoin out of ideology, curiosity or specific interests (such as innovators and enthusiasts) and the large mass of users who will only adopt the technology when it is perceived as safe, useful and easy to use. Bitcoin is at this critical point, at the beginning of the process of crossing the chasm.
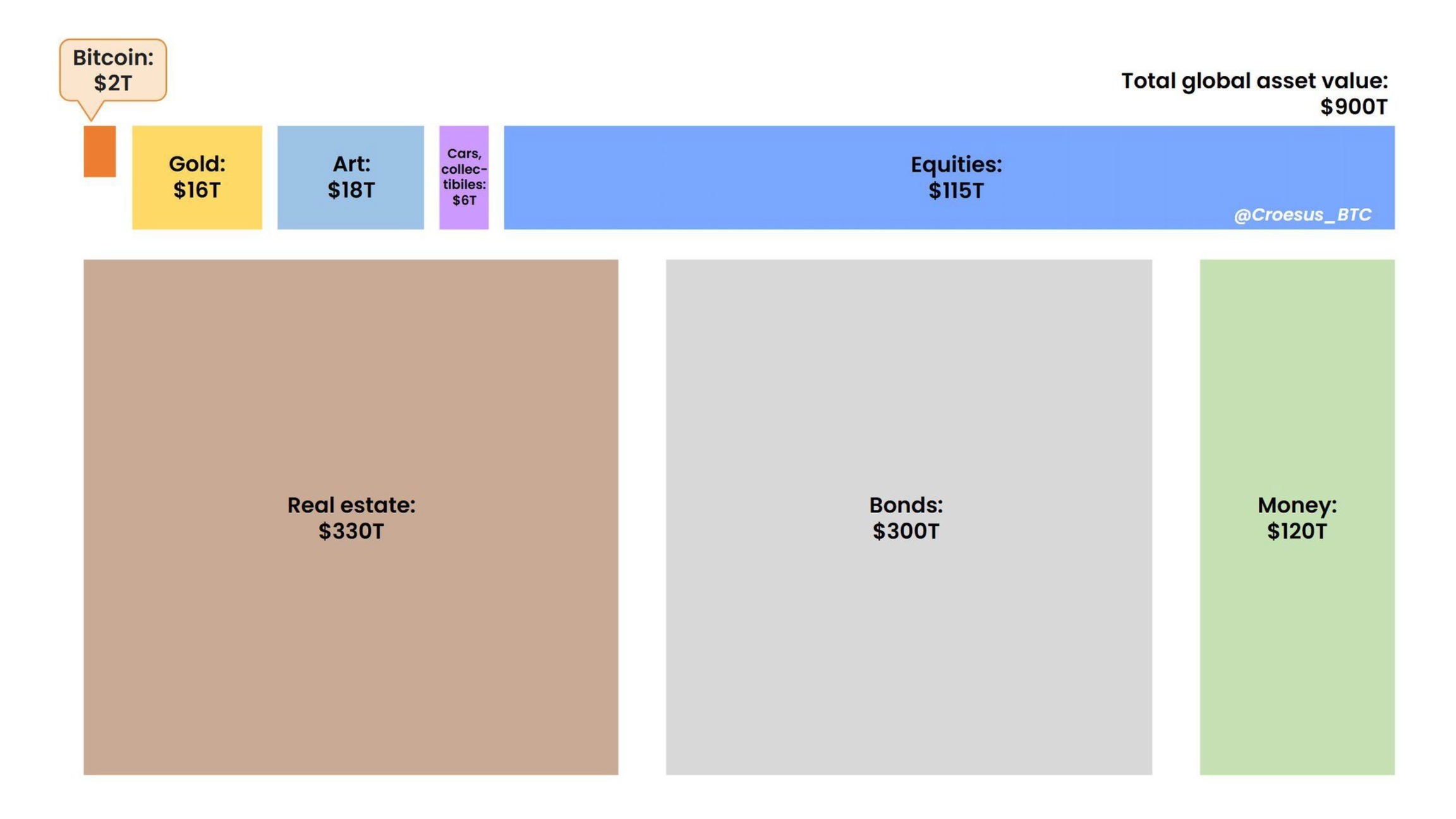
In fact, when we compare Bitcoin with other asset classes, it becomes clear how small it still is and the enormous potential for growth in market capitalization as more people adopt bitcoin as an asset and as money.
Here in this image we see how Bitcoin only has two trillion dollars in market capitalization, while other asset classes, such as real estate, stocks and gold, have tens or hundreds of trillions of dollars. 
Bitcoin is a new type of asset, money and a new financial system, decentralized and open source. If it continues on this trajectory, Bitcoin could reach or even surpass the market value of other traditional asset classes.

But the main point is that Bitcoin tends to continue appreciating because it is better money.
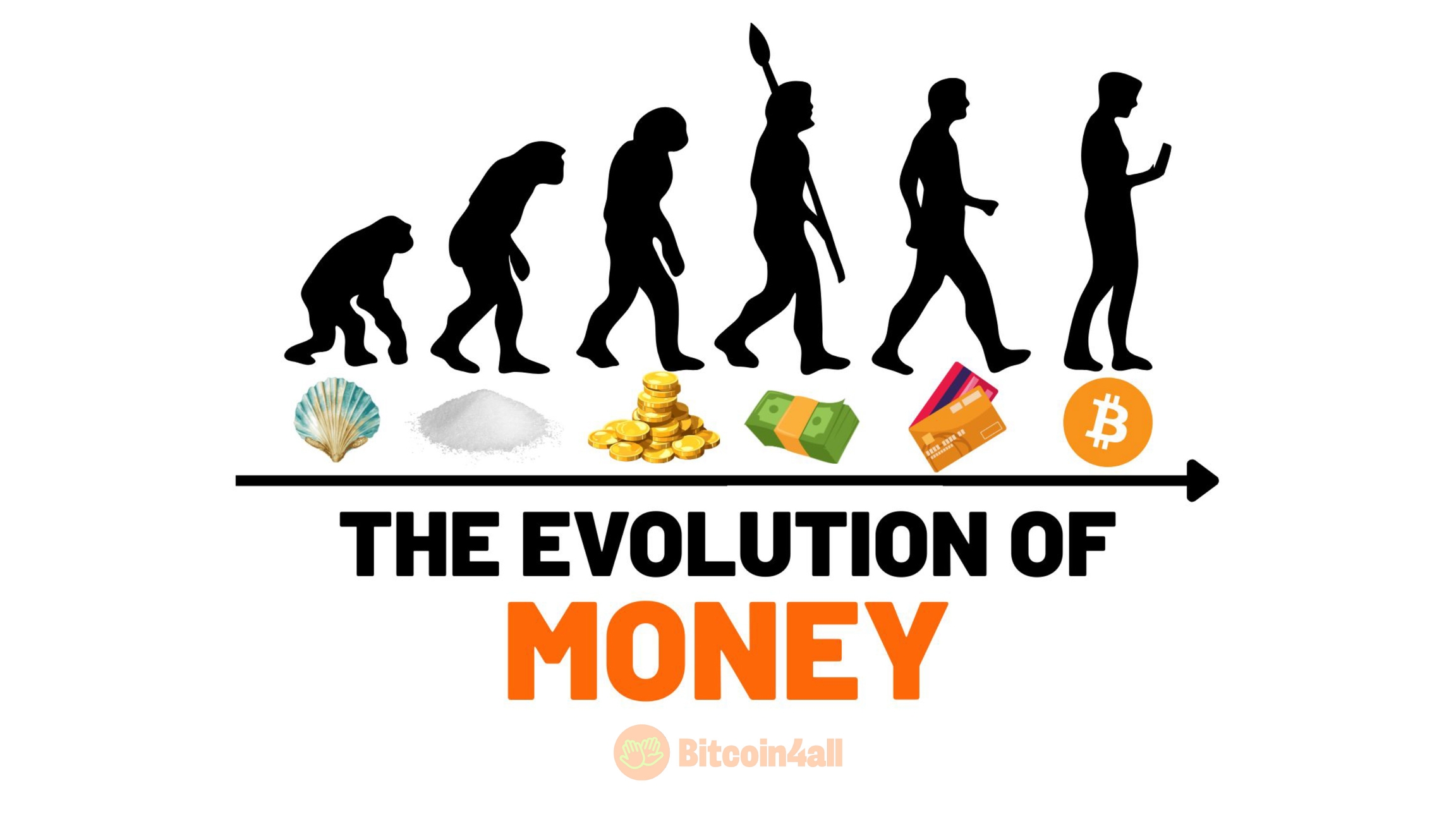
To understand why Bitcoin is better money, it is important to look at the evolution of money throughout history and how it has lost some of its fundamental properties. Bitcoin has the potential to rescue these essential properties and profoundly transform our relationship with money. It can revolutionize the way we save, invest and transact, offering an alternative that is transparent, resistant to manipulation and accessible to everyone.

Bitcoin solves many of the problems of the current financial system. Millions of people suffer from inflation, negative real interest rates, confiscation and even have their accounts closed by banks, and they don't even know that Bitcoin can be a solution to protect years of accumulated work that are being drained into melting government money like an ice cube.
In the next class, we will explore these problems in detail and you will understand why money, as we know it today, has literally been programmed to steal value from people without them realizing it.
See you next class!
Additional Resources
📢 Share this lesson!
Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Telegram
📈 Your Course Progress
Class 1 de 10 (10% completo)
Last updated
